|
The primary objective of monetary policy is to maintain ___ while supporting economic growth in the economy. |
Card: 1 / 34 |
|
True or False: Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) can engage in agricultural activities as their principal business. |
Card: 3 / 34 |
|
False; NBFCs cannot engage in agricultural activities as their principal business. |
Card: 4 / 34 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Reserve Bank of India was established on ___ under the provisions of the RBI Act, ___. |
Card: 5 / 34 |
|
The CRR is the percentage of a bank's total deposits that must be maintained with the RBI in cash form to ensure liquidity and control inflation. |
Card: 8 / 34 |
|
True or False: The Repo Rate is the interest rate at which the RBI pays to banks for short-term loans. |
Card: 9 / 34 |
|
False; The Repo Rate is the interest rate at which the RBI lends money to banks. |
Card: 10 / 34 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Basel III provisions emphasize the quality of capital by requiring banks to maintain a minimum ___ of ___ percent. |
Card: 11 / 34 |
|
What was the impact of the Banking Nationalisation Act of 1969 on the banking sector in India? |
Card: 13 / 34 |
|
The act led to the complete nationalization of 14 major commercial banks, aiming to align the banking sector with national economic goals and increase government control over the financial system. |
Card: 14 / 34 |
|
True or False: The Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) requires banks to maintain a portion of their net demand and time liabilities in cash. |
Card: 15 / 34 |
|
False; The SLR requires banks to maintain a portion of their net demand and time liabilities in liquid assets, not cash. |
Card: 16 / 34 |
|
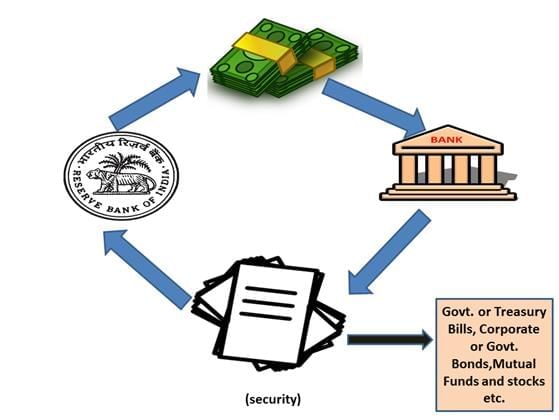
Fill in the blank: The Reserve Bank of India manages the ___ to stabilize the exchange rate of the Indian Rupee. |
Card: 17 / 34 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
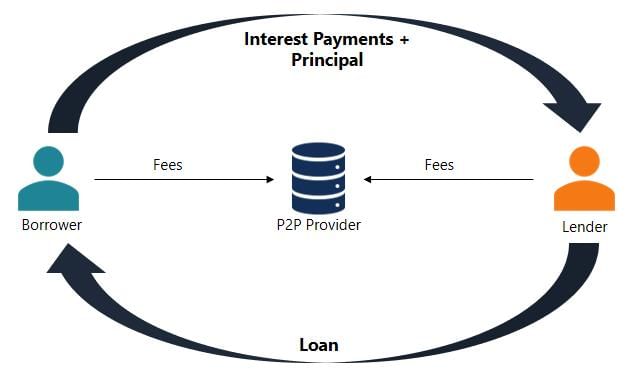
Fill in the blank: The RBI introduced the ____________ to promote financial inclusion and direct interaction between small lenders and borrowers. |
Card: 19 / 34 |
|
What is the primary purpose of the Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) in the Indian banking sector? |
Card: 21 / 34 |
|
ARCs are established to manage and resolve the burden of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) by purchasing bad loans from banks and attempting to recover them. |
Card: 22 / 34 |
|
True or False: The Marginal Cost of Funds-based Lending Rate (MCLR) was introduced to ensure that banks could lend at rates lower than the Base Rate. |
Card: 23 / 34 |
|
False; MCLR was introduced to improve the transparency and responsiveness of lending rates to changes in the monetary policy. |
Card: 24 / 34 |
|
What is the significance of the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) in the Indian banking system? |
Card: 25 / 34 |
|
LAF allows the RBI to adjust liquidity in the banking system by lending to or borrowing from banks at predetermined rates, ensuring stability in the money market. |
Card: 26 / 34 |
|
Fill in the blank: Under the ____________ scheme, banks can borrow overnight funds from the RBI at an interest rate higher than the repo rate. |
Card: 27 / 34 |
|
True or False: Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) can accept deposits and provide loans but cannot engage in agricultural activities as their principal business. |
Card: 29 / 34 |
|
The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is maintained by banks with the Reserve Bank of India and can be set between ___ and ___ percent. |
Card: 31 / 34 |
|
It acts as the regulator and supervisor of the financial system, managing monetary policy, currency issuance, and foreign exchange. |
Card: 34 / 34 |