|
Economic reforms in India began in ___ as a response to fiscal and balance-of-payment crises. |
Card: 1 / 32 |
|
True or False: The balance-of-payment crisis of 1991 was solely due to rising foreign debt. |
Card: 3 / 32 |
|
False. The crisis was also influenced by factors such as the First Gulf War and a high fiscal deficit. |
Card: 4 / 32 |
|
Fill in the blanks: Economic reforms in India were triggered by a balance-of-payment crisis and were largely influenced by the ___. |
Card: 5 / 32 |
|
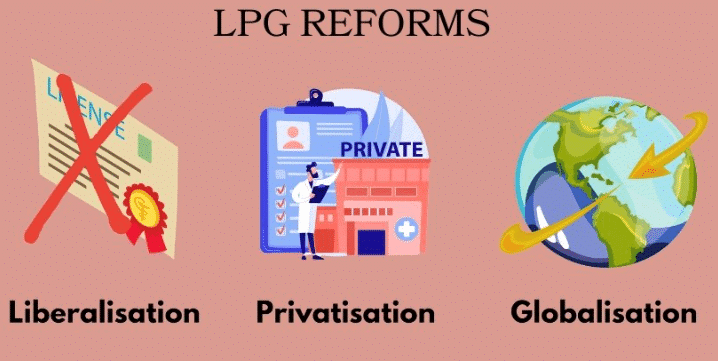
What are the two main categories of measures included in India's economic reform program? |
Card: 7 / 32 |
|
True or False: Liberalization in India means completely eliminating state control over the economy. |
Card: 11 / 32 |
|
False. Liberalization aims to reduce state control while finding a balance between state and market influences. |
Card: 12 / 32 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Third Generation reforms focus on achieving fully functional ___ to ensure inclusive development. |
Card: 13 / 32 |
|
True or False: Privatization refers to the government retaining full ownership of state-owned enterprises. |
Card: 15 / 32 |
|
False. Privatization involves transferring ownership of state-owned assets to the private sector. |
Card: 16 / 32 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Fill in the blank: The IMF conditions for India included devaluation of the rupee by ___%. |
Card: 17 / 32 |
|
True or False: The East Asian economies have struggled to achieve higher growth rates due to their economic reforms. |
Card: 19 / 32 |
|
False. East Asian economies have been successful in achieving higher growth rates and reducing poverty. |
Card: 20 / 32 |
|
What is the significance of structural reform measures in India's economic reforms? |
Card: 21 / 32 |
|
True or False: India's gradualist approach to economic reforms has resulted in immediate and significant economic outcomes. |
Card: 23 / 32 |
|
False. The gradualist approach has helped avoid instability but has not delivered desired outcomes quickly. |
Card: 24 / 32 |
|
It popularized the term globalization and emphasized the integration of economies. |
Card: 26 / 32 |
|
What was one of the main reasons for the introduction of the fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act? |
Card: 27 / 32 |
|
True or False: The Indian government's response to economic challenges has been solely reactive and has not included proactive measures. |
Card: 29 / 32 |
|
False. The government has adopted proactive measures, including transformational reforms. |
Card: 30 / 32 |
|
What is the ultimate goal of the IMF's involvement in India's economic reforms? |
Card: 31 / 32 |
|
To help India achieve balance in its balance-of-payment situation and make necessary adjustments. |
Card: 32 / 32 |