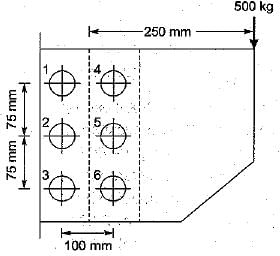
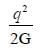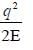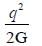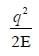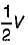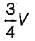All India Civil Engineering (CE) Group
If f(x) = 2x7+3x−5, which of the following is a factor of f(x)?- a)(x3+8)
- b)(x-1)
- c)(2x-5)
- d)(x+1)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If f(x) = 2x7+3x−5, which of the following is a factor of f(x)?
a)
(x3+8)
b)
(x-1)
c)
(2x-5)
d)
(x+1)

|
Anshu Kumar answered • 9 hours ago |
Understanding the Function f(x)
The function given is f(x) = 2x^7 + 3x - 5. To determine which of the options is a factor, we can use the Factor Theorem. This theorem states that if f(c) = 0 for some value c, then (x - c) is a factor of f(x).
Evaluating the Options
Let's evaluate each option by substituting the corresponding values into f(x):
The function given is f(x) = 2x^7 + 3x - 5. To determine which of the options is a factor, we can use the Factor Theorem. This theorem states that if f(c) = 0 for some value c, then (x - c) is a factor of f(x).
Evaluating the Options
Let's evaluate each option by substituting the corresponding values into f(x):
- Option A:
|
|
Priya Mehta
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:Statement-I: The Suposhit Maa Abhiyan is a maternal and child health initiative that aims to eliminate malnutrition among pregnant women and newborns through nutritional support, medical care, and health awareness.Statement-II: The Livestock Health and Disease Control Scheme (LHDCS) focuses on enhancing animal health, controlling livestock diseases, and improving veterinary services. Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
- b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
- c) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
- d) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: The Suposhit Maa Abhiyan is a maternal and child health initiative that aims to eliminate malnutrition among pregnant women and newborns through nutritional support, medical care, and health awareness.
Statement-II: The Livestock Health and Disease Control Scheme (LHDCS) focuses on enhancing animal health, controlling livestock diseases, and improving veterinary services.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
If the BOD of a diluted sample in 1 : 100 ratio is 11 PPM in the beginning and 8 PPM at the end of 5 days, then the BOD of the sample is- a)300 PPM
- b)950 PPM
- c)137.5 PPM
- d)73 PPM
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the BOD of a diluted sample in 1 : 100 ratio is 11 PPM in the beginning and 8 PPM at the end of 5 days, then the BOD of the sample is
a)
300 PPM
b)
950 PPM
c)
137.5 PPM
d)
73 PPM

|
Om Pillai answered • 15 hours ago |
Understanding BOD Calculation
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a critical parameter in assessing the organic pollution level in water. In this scenario, we analyze a diluted sample to determine the original BOD concentration.
Given Data
- Initial BOD of diluted sample: 11 PPM
- Final BOD after 5 days: 8 PPM
- Dilution factor: 1:100
Calculation Steps... more
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a critical parameter in assessing the organic pollution level in water. In this scenario, we analyze a diluted sample to determine the original BOD concentration.
Given Data
- Initial BOD of diluted sample: 11 PPM
- Final BOD after 5 days: 8 PPM
- Dilution factor: 1:100
Calculation Steps... more
|
|
Vaishnavi Saha
asked a question
|
Consider the following pairs:1. Suposhit Maa Abhiyan - Provides monthly nutrition kits of 17 kg to pregnant women2. Livestock Health and Disease Control Scheme (LHDCS) - Focuses on the eradication of livestock diseases through mass vaccination3. Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) - Provides interest subvention on loans up to ₹5 crore4. Suposhit Maa Abhiyan Phase 3 - Launched in February 2025How many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Suposhit Maa Abhiyan - Provides monthly nutrition kits of 17 kg to pregnant women
2. Livestock Health and Disease Control Scheme (LHDCS) - Focuses on the eradication of livestock diseases through mass vaccination
3. Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) - Provides interest subvention on loans up to ₹5 crore
4. Suposhit Maa Abhiyan Phase 3 - Launched in February 2025
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs
The effect of arching a beam, is- a)to reduce the bending moment throughout
- b)to increase the bending moment throughout
- c)nothing on the bending throughout
- d)all the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The effect of arching a beam, is
a)
to reduce the bending moment throughout
b)
to increase the bending moment throughout
c)
nothing on the bending throughout
d)
all the above.

|
Bibek Mukherjee answered • 17 hours ago |
Understanding Beam Arching
Arching a beam refers to the intentional curvature introduced into a beam's shape, which significantly influences its structural behavior, particularly concerning bending moments.
Reduction of Bending Moments
- When a beam is arched, it alters the distribution of internal forces.
- The curvature helps in redistributing loads applied to t... more
Arching a beam refers to the intentional curvature introduced into a beam's shape, which significantly influences its structural behavior, particularly concerning bending moments.
Reduction of Bending Moments
- When a beam is arched, it alters the distribution of internal forces.
- The curvature helps in redistributing loads applied to t... more
Cavity wall is generally provided for- a)heat insulation
- b)sound insulation
- c)prevention of dampness
- d)all the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cavity wall is generally provided for
a)
heat insulation
b)
sound insulation
c)
prevention of dampness
d)
all the above

|
Nilesh Kapoor answered • 20 hours ago |
Cavity Wall Overview
Cavity walls are a popular construction technique in modern buildings, designed with two separate wall sections (outer and inner) with a space or cavity in between. This design serves multiple purposes, making it a versatile choice for various climates and building requirements.
Heat Insulation
- Energy Efficiency: The cavity creates an air ... more
Cavity walls are a popular construction technique in modern buildings, designed with two separate wall sections (outer and inner) with a space or cavity in between. This design serves multiple purposes, making it a versatile choice for various climates and building requirements.
Heat Insulation
- Energy Efficiency: The cavity creates an air ... more
|
|
Sreemoyee Yadav
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements regarding the Suposhit Maa Abhiyan:1. The Suposhit Maa Abhiyan provides monthly nutrition kits weighing 17 kg to pregnant women.2. In Phase-III, the campaign focuses solely on the reduction of maternal mortality rates.3. The adoption model under the initiative allows multiple pregnant women per family to receive support.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)1 and 3 Only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding the Suposhit Maa Abhiyan:
1. The Suposhit Maa Abhiyan provides monthly nutrition kits weighing 17 kg to pregnant women.
2. In Phase-III, the campaign focuses solely on the reduction of maternal mortality rates.
3. The adoption model under the initiative allows multiple pregnant women per family to receive support.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
The steel used for rails under heavy traffic and on sharp curves, is- a)Nickel steel
- b)Chrome steel
- c)Magnese steel
- d)Vanadium steel
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The steel used for rails under heavy traffic and on sharp curves, is
a)
Nickel steel
b)
Chrome steel
c)
Magnese steel
d)
Vanadium steel

|
Varun Mukherjee answered • 22 hours ago |
Importance of Steel in Rail Construction
The type of steel used in rail construction is crucial, particularly for rails subjected to heavy traffic and sharp curves. The properties of steel must ensure durability, strength, and resistance to wear.
Why Manganese Steel?
Manganese steel, often referred to as Hadfield steel, is known for its unique properties that make it i... more
The type of steel used in rail construction is crucial, particularly for rails subjected to heavy traffic and sharp curves. The properties of steel must ensure durability, strength, and resistance to wear.
Why Manganese Steel?
Manganese steel, often referred to as Hadfield steel, is known for its unique properties that make it i... more
|
|
Aditi Ahuja
asked a question
|
What is the primary objective of the Suposhit Maa Abhiyan campaign launched by Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla in March 2020?- a)To provide financial assistance to pregnant women
- b)To enhance the health of pregnant women and newborns through nutritional support and medical care
- c)To promote gender equality in healthcare services
- d)To focus on improving childcare facilities across India
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary objective of the Suposhit Maa Abhiyan campaign launched by Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla in March 2020?
a)
To provide financial assistance to pregnant women
b)
To enhance the health of pregnant women and newborns through nutritional support and medical care
c)
To promote gender equality in healthcare services
d)
To focus on improving childcare facilities across India
|
|
Devansh Sen
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:Statement-I:
The discovery of Crassolabium dhritiae highlights the importance of nematodes in maintaining soil fertility.
Statement-II:
The NITI Aayog report underscores the urgent need for India to enhance its quantum computing capabilities for national security.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
- b)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
- c)Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
- d)Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
The discovery of Crassolabium dhritiae highlights the importance of nematodes in maintaining soil fertility.
Statement-II:
The NITI Aayog report underscores the urgent need for India to enhance its quantum computing capabilities for national security.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
The discovery of Crassolabium dhritiae highlights the importance of nematodes in maintaining soil fertility.
Statement-II:
The NITI Aayog report underscores the urgent need for India to enhance its quantum computing capabilities for national security.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Nilesh Datta
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:1. Crassolabium dhritiae is a newly discovered nematode species named in honor of the director of the Zoological Survey of India, Dhriti Banerjee.2. The species was discovered in the Himalayan biogeographic zone of India.3. Soil nematodes serve as valuable indicators of soil health due to their diverse feeding habits and sensitivity to environmental changes.- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)1 and 3 Only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Crassolabium dhritiae is a newly discovered nematode species named in honor of the director of the Zoological Survey of India, Dhriti Banerjee.
2. The species was discovered in the Himalayan biogeographic zone of India.
3. Soil nematodes serve as valuable indicators of soil health due to their diverse feeding habits and sensitivity to environmental changes.
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Kunal Joshi
asked a question
|
What is the significance of the discovery of the new nematode species, Crassolabium dhritiae, as mentioned in the text?- a)It enhances soil fertility and biodiversity.
- b)It poses a threat to existing nematode species.
- c)It primarily feeds on plant roots and fungi.
- d)It is the largest nematode species discovered to date.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the significance of the discovery of the new nematode species, Crassolabium dhritiae, as mentioned in the text?
a)
It enhances soil fertility and biodiversity.
b)
It poses a threat to existing nematode species.
c)
It primarily feeds on plant roots and fungi.
d)
It is the largest nematode species discovered to date.
|
|
Ashutosh Basu
asked a question
|
Consider the following pairs related to international agreements and geographical features:1. US-Ukraine Mineral Deal - Establishes a Reconstruction Investment Fund managed solely by the U.S.2. Indus River - Originates from the Pamir Mountains in Pakistan.3. Dnipro River - Flows through Ukraine and empties into the Caspian Sea.4. Ukraine's Mineral Reserves - Holds 5% of the world’s mineral resources, including 23 critical materials.How many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs related to international agreements and geographical features:
1. US-Ukraine Mineral Deal - Establishes a Reconstruction Investment Fund managed solely by the U.S.
2. Indus River - Originates from the Pamir Mountains in Pakistan.
3. Dnipro River - Flows through Ukraine and empties into the Caspian Sea.
4. Ukraine's Mineral Reserves - Holds 5% of the world’s mineral resources, including 23 critical materials.
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs
|
|
Abhishek Iyer
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements regarding the semi-cryogenic engine development by ISRO:1. The semi-cryogenic engine utilizes liquid hydrogen as fuel and liquid oxygen as an oxidizer.2. The semi-cryogenic engine is expected to enhance the payload capacity of ISRO's launch vehicles.3. Semi-cryogenic engines are lighter and easier to store than traditional cryogenic engines.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)1 and 3 Only
- d)2 and 3 Only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding the semi-cryogenic engine development by ISRO:
1. The semi-cryogenic engine utilizes liquid hydrogen as fuel and liquid oxygen as an oxidizer.
2. The semi-cryogenic engine is expected to enhance the payload capacity of ISRO's launch vehicles.
3. Semi-cryogenic engines are lighter and easier to store than traditional cryogenic engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
2 and 3 Only
|
|
Ayush Chawla
asked a question
|
What does the Wallace Line primarily represent in biogeography?- a) A physical barrier preventing all species migration
- b) A migration route for terrestrial mammals
- c) A geographical feature created by volcanic activity
- d) A boundary that demarcates different evolutionary histories of species
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the Wallace Line primarily represent in biogeography?
a)
A physical barrier preventing all species migration
b)
A migration route for terrestrial mammals
c)
A geographical feature created by volcanic activity
d)
A boundary that demarcates different evolutionary histories of species
|
|
Sagarika Dey
asked a question
|
What is the primary reason for the marbled cat's classification as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List?- a) Competition with larger wild cats
- b) Its small population size
- c) Its elusive nature and nocturnal behavior
- d) Habitat loss and fragmentation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary reason for the marbled cat's classification as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List?
a)
Competition with larger wild cats
b)
Its small population size
c)
Its elusive nature and nocturnal behavior
d)
Habitat loss and fragmentation

|
Mihir Kulkarni
asked a question
|
What is the primary goal of the Cities Coalition for Circularity (C-3)?- a) To create a political framework for global governance
- b) To focus solely on technological innovation in cities
- c) To promote sustainable urban development through city-to-city collaboration
- d) To eliminate all forms of urban development
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary goal of the Cities Coalition for Circularity (C-3)?
a)
To create a political framework for global governance
b)
To focus solely on technological innovation in cities
c)
To promote sustainable urban development through city-to-city collaboration
d)
To eliminate all forms of urban development
|
|
Arnav Trivedi
asked a question
|
What is a significant challenge facing the aviation partnership between India and the UAE?- a) Excessive international collaboration
- b) High ticket prices due to demand exceeding supply
- c) An abundance of available flights
- d) Decreased airport congestion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a significant challenge facing the aviation partnership between India and the UAE?
a)
Excessive international collaboration
b)
High ticket prices due to demand exceeding supply
c)
An abundance of available flights
d)
Decreased airport congestion
|
|
Omkar Rao
asked a question
|
What is the primary geological feature of Mount Erebus that distinguishes it from other volcanoes?- a) It features an active lava lake with alkalic lava
- b) It is dormant and has not erupted since 1972
- c) It has a caldera that is filled with water
- d) It is a shield volcano with low viscosity lava
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary geological feature of Mount Erebus that distinguishes it from other volcanoes?
a)
It features an active lava lake with alkalic lava
b)
It is dormant and has not erupted since 1972
c)
It has a caldera that is filled with water
d)
It is a shield volcano with low viscosity lava
|
|
Gauri Yadav
asked a question
|
What is a key feature of the Taurus KEPD-350 cruise missile that enhances its operational effectiveness?- a) It is designed to be launched from naval vessels.
- b) It operates exclusively at high altitudes.
- c) It is only effective during daylight operations.
- d) It has a modular design that allows for mission-specific customization.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a key feature of the Taurus KEPD-350 cruise missile that enhances its operational effectiveness?
a)
It is designed to be launched from naval vessels.
b)
It operates exclusively at high altitudes.
c)
It is only effective during daylight operations.
d)
It has a modular design that allows for mission-specific customization.
|
|
Vaani Malhotra
asked a question
|
What is a primary consequence of the spread of invasive plant species such as Ruellia elegans?- a) They outcompete native plants for essential resources.
- b) They enhance wildlife habitats.
- c) They promote biodiversity in local ecosystems.
- d) They increase the population of native flora.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a primary consequence of the spread of invasive plant species such as Ruellia elegans?
a)
They outcompete native plants for essential resources.
b)
They enhance wildlife habitats.
c)
They promote biodiversity in local ecosystems.
d)
They increase the population of native flora.
|
|
Wasima Thakur
asked a question
|
What is the primary goal of the Suposhit Maa Abhiyan initiative launched by Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla?- a) To eliminate malnutrition among pregnant women and newborns
- b) To increase the number of hospitals in rural areas
- c) To promote economic growth in Rajasthan
- d) To provide free education for children under five
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary goal of the Suposhit Maa Abhiyan initiative launched by Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla?
a)
To eliminate malnutrition among pregnant women and newborns
b)
To increase the number of hospitals in rural areas
c)
To promote economic growth in Rajasthan
d)
To provide free education for children under five
|
|
Ishan Shah
asked a question
|
What is the primary legal argument made by the Supreme Court regarding domicile-based reservations in medical admissions?- a) They ensure diversity in medical education.
- b) They violate the principle of equality before the law.
- c) They are essential for retaining medical professionals.
- d) They enhance local healthcare quality.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary legal argument made by the Supreme Court regarding domicile-based reservations in medical admissions?
a)
They ensure diversity in medical education.
b)
They violate the principle of equality before the law.
c)
They are essential for retaining medical professionals.
d)
They enhance local healthcare quality.
|
|
Aditi Verma
asked a question
|
What is the primary concern highlighted in the NITI Aayog's report regarding quantum computing and national security?- a) The historical development of encryption methods
- b) The potential environmental impact of quantum computing
- c) The cost of developing quantum hardware
- d) The strategic advantage of countries with quantum capabilities
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary concern highlighted in the NITI Aayog's report regarding quantum computing and national security?
a)
The historical development of encryption methods
b)
The potential environmental impact of quantum computing
c)
The cost of developing quantum hardware
d)
The strategic advantage of countries with quantum capabilities
|
|
Vihaan Gupta
asked a question
|
What is the significance of naming the newly discovered nematode species Crassolabium dhritiae?- a) It suggests the species is the largest of its kind.
- b) It reflects the geographic location of its discovery.
- c) It indicates the nematode's unique feeding habits.
- d) It honors a prominent zoologist for her contributions to the field.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the significance of naming the newly discovered nematode species Crassolabium dhritiae?
a)
It suggests the species is the largest of its kind.
b)
It reflects the geographic location of its discovery.
c)
It indicates the nematode's unique feeding habits.
d)
It honors a prominent zoologist for her contributions to the field.
|
|
Devang Choudhary
asked a question
|
What recent discovery in the Indus River bed is believed to have significant economic implications for Pakistan?- a) Substantial gold reserves
- b) Rich deposits of silver
- c) Large quantities of copper
- d) Abundant freshwater sources
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What recent discovery in the Indus River bed is believed to have significant economic implications for Pakistan?
a)
Substantial gold reserves
b)
Rich deposits of silver
c)
Large quantities of copper
d)
Abundant freshwater sources
|
|
Dhruv Kumar
asked a question
|
What is the primary purpose of the US-Ukraine Mineral Deal?- a) To grant the U.S. access to Ukraine's mineral reserves
- b) To establish a political alliance between Ukraine and the U.S.
- c) To create a joint military fund for defense cooperation
- d) To provide military support to Ukraine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary purpose of the US-Ukraine Mineral Deal?
a)
To grant the U.S. access to Ukraine's mineral reserves
b)
To establish a political alliance between Ukraine and the U.S.
c)
To create a joint military fund for defense cooperation
d)
To provide military support to Ukraine
|
|
Akshay Nair
asked a question
|
What advantage does the LOX-kerosene combination have over the LOX-liquid hydrogen combination in terms of performance?- a) It is more complex to manage.
- b) It provides a greater density impulse.
- c) It requires higher storage temperatures.
- d) It offers a lower density impulse.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What advantage does the LOX-kerosene combination have over the LOX-liquid hydrogen combination in terms of performance?
a)
It is more complex to manage.
b)
It provides a greater density impulse.
c)
It requires higher storage temperatures.
d)
It offers a lower density impulse.

|
Shubham Singh
asked a question
|
Consider the following pairs related to the Gupta Economy:1. Agriculture - Main occupation of the people2. Guild System - Declined during the Gupta period3. Gold Coins - Indicative of economic stability4. Crafts and Industries - Minimal role in economyHow many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs related to the Gupta Economy:
1. Agriculture - Main occupation of the people
2. Guild System - Declined during the Gupta period
3. Gold Coins - Indicative of economic stability
4. Crafts and Industries - Minimal role in economy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs

|
Work
asked a question
|
Consider the following pairs:1. Mercury - Smallest and closest to the sun2. Jupiter - Second largest planet with 12 satellites3. Uranus - Orbits around the sun in a clockwise direction from east to west4. Neptune - Natural satellite is the moonHow many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only two pairs
- b)Only one pair
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Mercury - Smallest and closest to the sun
2. Jupiter - Second largest planet with 12 satellites
3. Uranus - Orbits around the sun in a clockwise direction from east to west
4. Neptune - Natural satellite is the moon
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only two pairs
b)
Only one pair
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs

|
Abdul Raheman
asked a question
|
Based on the following rocks and minerals, select the correct statement.Quartz, shale, basalt, granite, marble, gypsum, mica- a)Basalt and marble are the only metamorphic rocks
- b)There is no sedimentary rock
- c)Granite is the only igneous rock
- d)Quartz and mica are minerals
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Based on the following rocks and minerals, select the correct statement.
Quartz, shale, basalt, granite, marble, gypsum, mica
a)
Basalt and marble are the only metamorphic rocks
b)
There is no sedimentary rock
c)
Granite is the only igneous rock
d)
Quartz and mica are minerals

|
Neha Turkar
asked a question
|
Among the more common varieties of timber namely sal, mango and deodar,1. Sal is strongest2. Mango is least durable3. Deodar is lightestOf the statements:- a)1 & 2 are correct
- b)1 & 3 are correct
- c)2 & 3 are correct
- d)1, 2 & 3 are correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the more common varieties of timber namely sal, mango and deodar,
1. Sal is strongest
2. Mango is least durable
3. Deodar is lightest
Of the statements:
a)
1 & 2 are correct
b)
1 & 3 are correct
c)
2 & 3 are correct
d)
1, 2 & 3 are correct

|
Vadde Sirivalli
asked a question
|
Directions to Solve Each of the following questions consists of a set of three figures X, Y and Z showing a sequence of folding of apiece of paper. Figure (Z) shows the manner in which the folded paper has been cut. These three figures are followed by four answer figures from which you have to choose a figure which would most closely resemble the unfolded form of figure (Z). Question - Choose a figure which would most closely resemble the unfolded form of Figure (Z).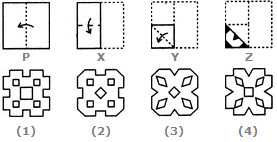
- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions to Solve
Each of the following questions consists of a set of three figures X, Y and Z showing a sequence of folding of apiece of paper. Figure (Z) shows the manner in which the folded paper has been cut. These three figures are followed by four answer figures from which you have to choose a figure which would most closely resemble the unfolded form of figure (Z).
Choose a figure which would most closely resemble the unfolded form of Figure (Z).

a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Rohan Singh
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:
- Statement I: The Great Granary in Mohenjodaro was built on a massive brick foundation and featured a central passageway.
- Statement II: The design of the Great Granary allowed for air circulation beneath the floor to keep the stored grain cool and dry.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
... more
Consider the following statements:
- Statement I: The Great Granary in Mohenjodaro was built on a massive brick foundation and featured a central passageway.
- Statement II: The design of the Great Granary allowed for air circulation beneath the floor to keep the stored grain cool and dry.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?

|
Rebecca Surin
asked a question
|
Oceans distant from deserts or with limited accessibility to dust-carrying winds from deserts often have limited primary productivity. This is due to - a) Lack of iron nutrient supplies
- b) Presence of kelp forests (macroalgae) in such areas
- c) Absence of a Photic Zone
- d) Warm water temperature
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oceans distant from deserts or with limited accessibility to dust-carrying winds from deserts often have limited primary productivity. This is due to
a)
Lack of iron nutrient supplies
b)
Presence of kelp forests (macroalgae) in such areas
c)
Absence of a Photic Zone
d)
Warm water temperature

|
Moachuba Pongener
asked a question
|
For a continuous R.C. beam, match List-I (Condition) with List-II (Placement of live load) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists.
List-I
A. For maximum sagging moment in a span
B. For maximum hogging moment at a support
C. For maximum hogging moment in a span
List-II
1. The span adjoining the span as well as alternate span
2. The same span as well as alternate spans
3. The adjacent spans on both sides of this support as well as spans alternate to these
4. Spans next to the adjacent spans of the support plus alternate spans
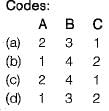
- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For a continuous R.C. beam, match List-I (Condition) with List-II (Placement of live load) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists.
List-I
A. For maximum sagging moment in a span
B. For maximum hogging moment at a support
C. For maximum hogging moment in a span
List-II
1. The span adjoining the span as well as alternate span
2. The same span as well as alternate spans
3. The adjacent spans on both sides of this support as well as spans alternate to these
4. Spans next to the adjacent spans of the support plus alternate spans

List-I
A. For maximum sagging moment in a span
B. For maximum hogging moment at a support
C. For maximum hogging moment in a span
List-II
1. The span adjoining the span as well as alternate span
2. The same span as well as alternate spans
3. The adjacent spans on both sides of this support as well as spans alternate to these
4. Spans next to the adjacent spans of the support plus alternate spans

a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D

|
Malavika Basak
asked a question
|
These questions are based on the following information. P, Q, R, S and T sit around a table. P sits two seats to the left of R and Q sits two seats to the right of R.Q. If a new person U joins the group such that the initial conditions for the seating arrangement should be observed and also a new condition that U does not sit next to P, S or T be satisfied, then who will be the neighbours of P (one on either side)?- a)T and Q
- b)S and Q
- c)T and R
- d)R and Q
- e)S and T
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
These questions are based on the following information. P, Q, R, S and T sit around a table. P sits two seats to the left of R and Q sits two seats to the right of R.
Q. If a new person U joins the group such that the initial conditions for the seating arrangement should be observed and also a new condition that U does not sit next to P, S or T be satisfied, then who will be the neighbours of P (one on either side)?
a)
T and Q
b)
S and Q
c)
T and R
d)
R and Q
e)
S and T

|
Rony Ahmed
asked a question
|
Two places A and B are at a certain distance. Ramu started from A towards B at a speed of 40 kmph. After 2 hours Raju started from B towards A at a speed of 60 kmph. If they meet at a place C then ratio of ratio of time taken by Raju to Ramu to reach Place C is 2:3. Then what is the distance between A and B?
- a) 300 Km
- b) 400 Km
- c) 480 Km
- d) 600 Km
- e) Cannot be determined
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two places A and B are at a certain distance. Ramu started from A towards B at a speed of 40 kmph. After 2 hours Raju started from B towards A at a speed of 60 kmph. If they meet at a place C then ratio of ratio of time taken by Raju to Ramu to reach Place C is 2:3. Then what is the distance between A and B?
a)
300 Kmb)
400 Kmc)
480 Kmd)
600 Kme)
Cannot be determined

|
Abhishek Sharma
asked a question
|
One of the Lehmann's rules of plane tabling, is- a)location of the instrument station is alwaysdistant from each of the three rays from theknown points in proportion to theirdistances
- b)When looking in the direction of each ofthe given points, the instrument station willbe on the right side of one and left side ofthe other ray
- c)when the instrument station is outside thecircumscribing circle its location is alwayson the opposite side of the ray to the mostdistant point as the inter section of the othertwo rays
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the Lehmann's rules of plane tabling, is
a)
location of the instrument station is alwaysdistant from each of the three rays from theknown points in proportion to theirdistances
b)
When looking in the direction of each ofthe given points, the instrument station willbe on the right side of one and left side ofthe other ray
c)
when the instrument station is outside thecircumscribing circle its location is alwayson the opposite side of the ray to the mostdistant point as the inter section of the othertwo rays
d)
none of these

|
Manu Lalam
asked a question
|
A car started from Indore to Bhopal at a certain speed. The Car missed an accident at 40Kms away from Indore, then the driver decided to reduce Car speed to 4/5 of the original speed. Due to this, he reached Bhopal by a late of 1hr 15min.Suppose if he missed an accident at 80Km away from Indore and from then he maintained 4/5 of original speed then he would reach Bhopal by a late of 1hour. Then what is the original speed of the Car?- a)20 km/hr
- b)40 km/hr
- c)60 km/hr
- d)80 km/hr
- e)Cannot be determined
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A car started from Indore to Bhopal at a certain speed. The Car missed an accident at 40Kms away from Indore, then the driver decided to reduce Car speed to 4/5 of the original speed. Due to this, he reached Bhopal by a late of 1hr 15min.Suppose if he missed an accident at 80Km away from Indore and from then he maintained 4/5 of original speed then he would reach Bhopal by a late of 1hour. Then what is the original speed of the Car?
a)
20 km/hr
b)
40 km/hr
c)
60 km/hr
d)
80 km/hr
e)
Cannot be determined
|
|
Mihir Iyer
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:1. The first discovery of rock paintings in India was made in 1867-68 by Archaeologist Archibold Carlleyle.2. Bhimbetka Caves, discovered in 1957-58, exhibit nearly 400 painted rock shelters in five clusters.3. The Upper Palaeolithic period is characterized by the artistic depiction of simple human figures, activities, geometric designs, and symbols.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)1 and 3 Only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. The first discovery of rock paintings in India was made in 1867-68 by Archaeologist Archibold Carlleyle.
2. Bhimbetka Caves, discovered in 1957-58, exhibit nearly 400 painted rock shelters in five clusters.
3. The Upper Palaeolithic period is characterized by the artistic depiction of simple human figures, activities, geometric designs, and symbols.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Ashwin Desai
asked a question
|
In each of the questions, a word/phrase has been used in sentences in five different ways. Choose the option corresponding to the sentence in which the usage of the word/phrase is incorrect or inappropriate.Buckle- a)After the long hike our knees were beginning to buckle.
- b)The horse suddenly broke into a buckle.
- c)The accused did not buckle under police interrogation.
- d)Sometimes, an earthquake can make a bridge buckle.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In each of the questions, a word/phrase has been used in sentences in five different ways. Choose the option corresponding to the sentence in which the usage of the word/phrase is incorrect or inappropriate.
Buckle
a)
After the long hike our knees were beginning to buckle.
b)
The horse suddenly broke into a buckle.
c)
The accused did not buckle under police interrogation.
d)
Sometimes, an earthquake can make a bridge buckle.

|
Arun Kumar
asked a question
|
Pick up the correct statement from the following:Method of sawing timber- a)tangentially to annual rings, is known astangential method.
- b)in four quarters such that each board cutsannual rings at angles not less than 45º, isknown as quarter sawing method.
- c)cut out of quarter logs, parallel to themedullary rays and perpendicular to annualrings, is known as radial sawaing
- d)all the above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick up the correct statement from the following:Method of sawing timber
a)
tangentially to annual rings, is known astangential method.
b)
in four quarters such that each board cutsannual rings at angles not less than 45º, isknown as quarter sawing method.
c)
cut out of quarter logs, parallel to themedullary rays and perpendicular to annualrings, is known as radial sawaing
d)
all the above.

|
Shruti Patil
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:
- The Harappans were the earliest people to produce cotton, known to Greeks as sindon.
- The Harappan Civilization was horse-centered, with evidence of horses found in all major Harappan sites.
- Seals are considered the greatest artistic creations of the Harappan culture.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- a)Only two
- b)Only one
- c)All three
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
- The Harappans were the earliest people to produce cotton, known to Greeks as sindon.
- The Harappan Civilization was horse-centered, with evidence of horses found in all major Harappan sites.
- Seals are considered the greatest artistic creations of the Harappan culture.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
a)
Only two
b)
Only one
c)
All three
d)
None

|
Garima Basak
asked a question
|
In Boussinesq’s solution to the problem of stress distribution, all the following assumptions are made, except:- a)Soil mass is semi-infinite
- b)The elastic modulus of soil is constant
- c)Soil is homogeneous
- d)Soil is anisotropic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In Boussinesq’s solution to the problem of stress distribution, all the following assumptions are made, except:
a)
Soil mass is semi-infinite
b)
The elastic modulus of soil is constant
c)
Soil is homogeneous
d)
Soil is anisotropic
|
|
Rajeev Verma
asked a question
|
Consider the following pairs regarding the Gond Tribes:1. Raj Gonds - Predominantly found in Madhya Pradesh2. Madia Gonds - Known for their historic forts and palaces3. Dhurve Gonds - Primarily practice agriculture4. Khatulwar Gonds - Speak the Telugu languageHow many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs regarding the Gond Tribes:
1. Raj Gonds - Predominantly found in Madhya Pradesh
2. Madia Gonds - Known for their historic forts and palaces
3. Dhurve Gonds - Primarily practice agriculture
4. Khatulwar Gonds - Speak the Telugu language
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs
|
|
Ankit Nambiar
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements regarding the Wallace Line:1. The Wallace Line serves as a biogeographical boundary that distinctly separates the flora and fauna of Asia and Australia.2. Species migration across the Wallace Line is common for both terrestrial and marine life.3. The Wallace Line was identified by Alfred Russel Wallace in the 20th century.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)1 and 3 Only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding the Wallace Line:
1. The Wallace Line serves as a biogeographical boundary that distinctly separates the flora and fauna of Asia and Australia.
2. Species migration across the Wallace Line is common for both terrestrial and marine life.
3. The Wallace Line was identified by Alfred Russel Wallace in the 20th century.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Arnav Saha
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements regarding the Marbled Cat and its habitat:1. The marbled cat (Pardofelis marmorata) is classified as Near Threatened (NT) on the IUCN Red List due to habitat loss and is listed in CITES Appendix I.2. Dehing Patkai National Park, where the marbled cat was recently spotted, is located in the Dibrugarh district of Assam and was designated as a national park in 2020.3. The marbled cat is primarily diurnal and is most active during the day.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)1 and 3 Only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding the Marbled Cat and its habitat:
1. The marbled cat (Pardofelis marmorata) is classified as Near Threatened (NT) on the IUCN Red List due to habitat loss and is listed in CITES Appendix I.
2. Dehing Patkai National Park, where the marbled cat was recently spotted, is located in the Dibrugarh district of Assam and was designated as a national park in 2020.
3. The marbled cat is primarily diurnal and is most active during the day.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3
Fetching relevant content for you
Ask a doubt
Recommended Content
|
|
|
|
|