Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h...
Start Learning for Free
On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol
Most Upvoted Answer
On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was ...
Calculation of Molar Mass of Solute
Given:
- Mass of solute (m) = 2.34g
- Mass of solvent (M) = 40g
- Boiling point elevation (ΔTb) = 0.81K
- Boiling point constant (Kb) = 2.53Kkg/mol
Formula:
ΔTb = Kb × m / W2
where W2 = mass of solvent in kg
m = molality of solution
molality (m) = moles of solute / mass of solvent in kg
molar mass of solute = mass of solute / moles of solute
Solution:
First, we need to find the molality of the solution using the given data:
ΔTb = Kb × m / W2
0.81 = 2.53 × m / 0.04
m = 0.0321 mol/kg
Now, we can find the moles of solute:
molality (m) = moles of solute / mass of solvent in kg
0.0321 = moles of solute / 0.04
moles of solute = 0.001284 mol
Finally, we can find the molar mass of the solute:
molar mass of solute = mass of solute / moles of solute
molar mass of solute = 2.34g / 0.001284 mol
molar mass of solute = 1821.05 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of the solute is 1821.05 g/mol.
Explanation:
When a solute is dissolved in a solvent, the boiling point of the resulting solution is higher than that of the pure solvent. This is known as boiling point elevation and is directly proportional to the molality of the solution. The proportionality constant is known as the boiling point constant (Kb).
The formula used to calculate the molar mass of the solute is based on the fact that molality is the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. By calculating the molality of the solution, we can find the number of moles of solute. Dividing the mass of solute by the number of moles of solute gives us the molar mass of the solute.
In this case, we are given the mass of solute, mass of solvent, boiling point elevation, and boiling point constant. By using the formula and substituting the given values, we can calculate the molality of the solution. From there, we can find the number of moles of solute and finally the molar mass of the solute.
Given:
- Mass of solute (m) = 2.34g
- Mass of solvent (M) = 40g
- Boiling point elevation (ΔTb) = 0.81K
- Boiling point constant (Kb) = 2.53Kkg/mol
Formula:
ΔTb = Kb × m / W2
where W2 = mass of solvent in kg
m = molality of solution
molality (m) = moles of solute / mass of solvent in kg
molar mass of solute = mass of solute / moles of solute
Solution:
First, we need to find the molality of the solution using the given data:
ΔTb = Kb × m / W2
0.81 = 2.53 × m / 0.04
m = 0.0321 mol/kg
Now, we can find the moles of solute:
molality (m) = moles of solute / mass of solvent in kg
0.0321 = moles of solute / 0.04
moles of solute = 0.001284 mol
Finally, we can find the molar mass of the solute:
molar mass of solute = mass of solute / moles of solute
molar mass of solute = 2.34g / 0.001284 mol
molar mass of solute = 1821.05 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of the solute is 1821.05 g/mol.
Explanation:
When a solute is dissolved in a solvent, the boiling point of the resulting solution is higher than that of the pure solvent. This is known as boiling point elevation and is directly proportional to the molality of the solution. The proportionality constant is known as the boiling point constant (Kb).
The formula used to calculate the molar mass of the solute is based on the fact that molality is the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. By calculating the molality of the solution, we can find the number of moles of solute. Dividing the mass of solute by the number of moles of solute gives us the molar mass of the solute.
In this case, we are given the mass of solute, mass of solvent, boiling point elevation, and boiling point constant. By using the formula and substituting the given values, we can calculate the molality of the solution. From there, we can find the number of moles of solute and finally the molar mass of the solute.
Community Answer
On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was ...
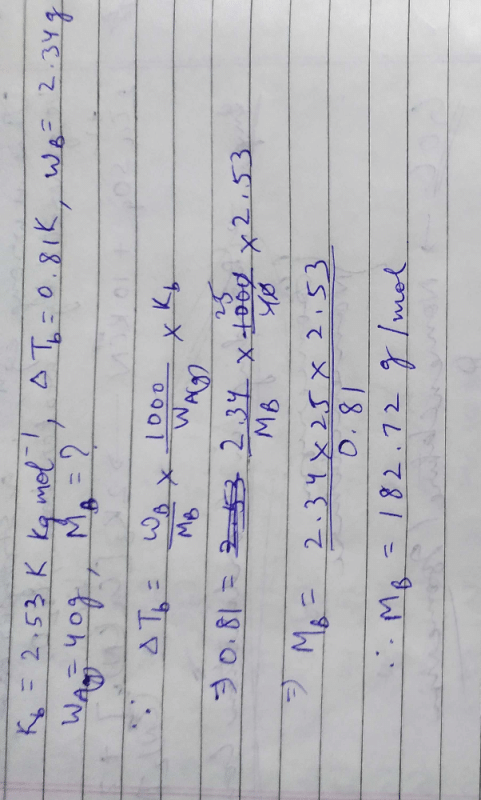

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol
Question Description
On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol.
On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol.
Solutions for On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol, a detailed solution for On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol has been provided alongside types of On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice On dissoliving 2.34gm of solute in 40g of c6h6 the BP of solution was higher than that of benzene of 0.81k calculate the molar mass of solute given kb=2.53kkg/mol tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















