JEE Exam > JEE Questions > What is apex angle
Start Learning for Free
What is apex angle
Verified Answer
What is apex angle
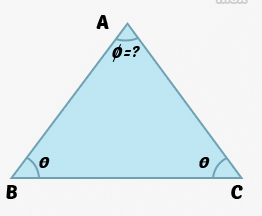
In an Isosceles triangle, the two equal sides are called legs and the third side is called as base. The angle which is opposite to the base is called the vertex angle and the point associated with that angle is called as apex. Apex angle of Isosceles triangle is the angle between the lines that joins the pointed end. Use this online calculator to find the apex angle with the given base angle.
Φ = 180 - (2*θ)
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is apex angle
The apex is the pointed tip of a cone. The apex angle is the angle between the lines that define the apex
Community Answer
What is apex angle
Apex Angle: Explained in Detail
An apex angle is a term used in geometry to describe the angle formed at the apex, or the vertex, of a shape or figure. It is the angle created by two lines or surfaces that meet at a common point, known as the apex. The apex angle is an important concept in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering. Understanding apex angles is crucial for analyzing and measuring different geometrical structures and their properties.
Key Points:
- Apex angle is the angle formed at the apex or vertex of a shape or figure.
- It is created by two lines or surfaces that meet at a common point.
- Apex angles have applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
Properties of Apex Angles:
Apex angles possess certain properties that are essential to comprehend their behavior and applications. Let's explore some of these properties:
1. Measurement: The measurement of an apex angle is typically given in degrees (°) or radians (rad). It represents the amount of rotation between the two lines or surfaces that meet at the apex.
2. Types of Apex Angles: Apex angles can be classified into different types based on their measurements. Some common types include acute angle (less than 90°), right angle (exactly 90°), obtuse angle (greater than 90° but less than 180°), and straight angle (exactly 180°).
3. Sum of Apex Angles: In certain geometric shapes, such as triangles or polygons, the sum of the apex angles is constant. For example, in a triangle, the sum of all three apex angles always equals 180°.
4. Apex Angles in Polyhedra: Polyhedra, three-dimensional shapes with flat faces and straight edges, also have apex angles. The apex angles of polyhedra depend on the specific shape and the number of faces meeting at each vertex.
Applications:
The concept of apex angles finds numerous applications in various fields, including:
1. Architecture and Engineering: Apex angles are crucial in designing and constructing structures. Architects and engineers utilize apex angles to determine the stability, strength, and load-bearing capacity of buildings and bridges.
2. Optics: In optics, apex angles play a significant role in understanding and analyzing the behavior of light rays as they pass through different materials or reflect off surfaces. The apex angle of a prism, for instance, determines the deviation and dispersion of light.
3. Crystallography: The study of crystal structures heavily relies on apex angles. The angles between different crystal faces help identify and classify various crystal structures.
4. Astronomy: Apex angles are used in astronomy to calculate the inclination and orientation of celestial bodies, such as planets, moons, and asteroids.
In conclusion, the apex angle is a fundamental concept in geometry that describes the angle formed at the apex or vertex of a shape or figure. It has diverse applications across multiple disciplines, including mathematics, physics, engineering, architecture, optics, crystallography, and astronomy. Understanding apex angles allows for the analysis, measurement, and prediction of various geometrical structures and their properties.
An apex angle is a term used in geometry to describe the angle formed at the apex, or the vertex, of a shape or figure. It is the angle created by two lines or surfaces that meet at a common point, known as the apex. The apex angle is an important concept in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering. Understanding apex angles is crucial for analyzing and measuring different geometrical structures and their properties.
Key Points:
- Apex angle is the angle formed at the apex or vertex of a shape or figure.
- It is created by two lines or surfaces that meet at a common point.
- Apex angles have applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
Properties of Apex Angles:
Apex angles possess certain properties that are essential to comprehend their behavior and applications. Let's explore some of these properties:
1. Measurement: The measurement of an apex angle is typically given in degrees (°) or radians (rad). It represents the amount of rotation between the two lines or surfaces that meet at the apex.
2. Types of Apex Angles: Apex angles can be classified into different types based on their measurements. Some common types include acute angle (less than 90°), right angle (exactly 90°), obtuse angle (greater than 90° but less than 180°), and straight angle (exactly 180°).
3. Sum of Apex Angles: In certain geometric shapes, such as triangles or polygons, the sum of the apex angles is constant. For example, in a triangle, the sum of all three apex angles always equals 180°.
4. Apex Angles in Polyhedra: Polyhedra, three-dimensional shapes with flat faces and straight edges, also have apex angles. The apex angles of polyhedra depend on the specific shape and the number of faces meeting at each vertex.
Applications:
The concept of apex angles finds numerous applications in various fields, including:
1. Architecture and Engineering: Apex angles are crucial in designing and constructing structures. Architects and engineers utilize apex angles to determine the stability, strength, and load-bearing capacity of buildings and bridges.
2. Optics: In optics, apex angles play a significant role in understanding and analyzing the behavior of light rays as they pass through different materials or reflect off surfaces. The apex angle of a prism, for instance, determines the deviation and dispersion of light.
3. Crystallography: The study of crystal structures heavily relies on apex angles. The angles between different crystal faces help identify and classify various crystal structures.
4. Astronomy: Apex angles are used in astronomy to calculate the inclination and orientation of celestial bodies, such as planets, moons, and asteroids.
In conclusion, the apex angle is a fundamental concept in geometry that describes the angle formed at the apex or vertex of a shape or figure. It has diverse applications across multiple disciplines, including mathematics, physics, engineering, architecture, optics, crystallography, and astronomy. Understanding apex angles allows for the analysis, measurement, and prediction of various geometrical structures and their properties.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Question Description
What is apex angle for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about What is apex angle covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is apex angle.
What is apex angle for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about What is apex angle covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is apex angle.
Solutions for What is apex angle in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is apex angle defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is apex angle, a detailed solution for What is apex angle has been provided alongside types of What is apex angle theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is apex angle tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



























