Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > An example for bidentate and negatively charg...
Start Learning for Free
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand is
- a)acetylacetonate (acac)
- b)propylene diamine (pn)
- c)ethylene diamine (en)
- d)bipyridyl (bip
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylaceto...
CH3COCH2COCH3
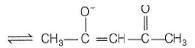
It can ligate through two oxygen atoms.
Most Upvoted Answer
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylaceto...
Bidentate and negatively charged ligands are molecules or ions that have two donor atoms capable of forming two coordination bonds with a central metal ion and carry a negative charge. These ligands play a crucial role in coordination chemistry as they can form stable complexes with metal ions due to their ability to donate electrons.
The given options for bidentate and negatively charged ligands are:
a) Acetylacetonate (acac):
- Acetylacetonate is a bidentate ligand that contains two oxygen atoms capable of donating a pair of electrons to form coordination bonds with a metal ion.
- It carries a negative charge due to the presence of two additional electron-donating groups (CH3) on the molecule.
- The negatively charged acetylacetonate ion (acac-) can coordinate with a metal ion by donating its lone pairs of electrons to form stable complexes.
b) Propylene diamine (pn):
- Propylene diamine is a bidentate ligand that contains two nitrogen atoms capable of donating a pair of electrons to form coordination bonds with a metal ion.
- However, it does not carry a negative charge.
c) Ethylene diamine (en):
- Ethylene diamine is a bidentate ligand that contains two nitrogen atoms capable of donating a pair of electrons to form coordination bonds with a metal ion.
- However, it does not carry a negative charge.
d) Bipyridyl (bip):
- Bipyridyl is a bidentate ligand that contains two nitrogen atoms capable of donating a pair of electrons to form coordination bonds with a metal ion.
- It does not carry a negative charge.
Among the given options, only acetylacetonate (acac) satisfies both criteria of being bidentate and negatively charged. It has two oxygen atoms capable of forming coordination bonds and carries a negative charge due to the presence of additional electron-donating groups. Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer.
This information is crucial in understanding the chemical behavior and reactivity of coordination compounds, as different ligands can influence the properties and stability of the resulting complexes.
The given options for bidentate and negatively charged ligands are:
a) Acetylacetonate (acac):
- Acetylacetonate is a bidentate ligand that contains two oxygen atoms capable of donating a pair of electrons to form coordination bonds with a metal ion.
- It carries a negative charge due to the presence of two additional electron-donating groups (CH3) on the molecule.
- The negatively charged acetylacetonate ion (acac-) can coordinate with a metal ion by donating its lone pairs of electrons to form stable complexes.
b) Propylene diamine (pn):
- Propylene diamine is a bidentate ligand that contains two nitrogen atoms capable of donating a pair of electrons to form coordination bonds with a metal ion.
- However, it does not carry a negative charge.
c) Ethylene diamine (en):
- Ethylene diamine is a bidentate ligand that contains two nitrogen atoms capable of donating a pair of electrons to form coordination bonds with a metal ion.
- However, it does not carry a negative charge.
d) Bipyridyl (bip):
- Bipyridyl is a bidentate ligand that contains two nitrogen atoms capable of donating a pair of electrons to form coordination bonds with a metal ion.
- It does not carry a negative charge.
Among the given options, only acetylacetonate (acac) satisfies both criteria of being bidentate and negatively charged. It has two oxygen atoms capable of forming coordination bonds and carries a negative charge due to the presence of additional electron-donating groups. Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer.
This information is crucial in understanding the chemical behavior and reactivity of coordination compounds, as different ligands can influence the properties and stability of the resulting complexes.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylaceto...
Open c is also rgt I think

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand isa)acetylacetonate (acac)b)propylene diamine (pn)c)ethylene diamine (en)d)bipyridyl (bipCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















