Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)he...
Start Learning for Free
EDTA is a ........ligand.
- a)monodentate
- b)hexadentate
- c)bidentate
- d)tridentate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)...
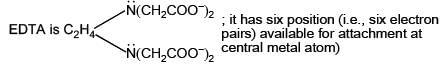
Most Upvoted Answer
EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)...
EDTA, a hexadentate ligand, is an example of a polydentate ligand that has six donor atoms with electron pairs that can be used to bond to a central metal atom or ion.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)...
Explanation:
EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is a chelating agent widely used in analytical chemistry and biochemistry. It forms complexes with metal ions that are typically six-coordinate, with EDTA acting as a hexadentate ligand. This means that EDTA has six donor atoms (four carboxylate groups and two amine groups) that can bind to a metal ion.
The coordination of EDTA to a metal ion involves the formation of coordinate covalent bonds, in which the lone pair electrons on the donor atoms of EDTA are shared with the metal ion. The resulting complex is a stable, water-soluble species with a high degree of structural integrity.
EDTA is a highly effective chelating agent due to its ability to form complexes with a wide range of metal ions, including those that are highly toxic or that form insoluble salts. This property makes EDTA a valuable tool in many industrial and environmental applications, including wastewater treatment, heavy metal remediation, and metal recovery.
In summary, EDTA is a hexadentate ligand due to its ability to coordinate to a metal ion through six donor atoms. This property makes it a highly effective chelating agent with many diverse applications.
EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is a chelating agent widely used in analytical chemistry and biochemistry. It forms complexes with metal ions that are typically six-coordinate, with EDTA acting as a hexadentate ligand. This means that EDTA has six donor atoms (four carboxylate groups and two amine groups) that can bind to a metal ion.
The coordination of EDTA to a metal ion involves the formation of coordinate covalent bonds, in which the lone pair electrons on the donor atoms of EDTA are shared with the metal ion. The resulting complex is a stable, water-soluble species with a high degree of structural integrity.
EDTA is a highly effective chelating agent due to its ability to form complexes with a wide range of metal ions, including those that are highly toxic or that form insoluble salts. This property makes EDTA a valuable tool in many industrial and environmental applications, including wastewater treatment, heavy metal remediation, and metal recovery.
In summary, EDTA is a hexadentate ligand due to its ability to coordinate to a metal ion through six donor atoms. This property makes it a highly effective chelating agent with many diverse applications.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice EDTA is a ........ligand. a)monodentate b)hexadentate c)bidentate d)tridentateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















