B Com Exam > B Com Questions > how financial market achieve equilibrium Rela...
Start Learning for Free
how financial market achieve equilibrium
?Most Upvoted Answer
how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Fina...
equilibrium conditions- where money supply equals money demand
money supply generally given as a constant (vertical line)
doesn't change w/ interest rate
Ms = Md
Md / $Y = L(i)
Md / $Y - ratio of money demand to nominal income (fraction of total income that ppl hold as money)
LM relation - equilibrium at intersection of money supply and money demand (downward sloping curve dependent on interest rate i from L(i))
interest at level that that cause ppl to hold Md equal to Ms
if Md=Ms then Bd=Bs since (wealth = B+D and wealth stays constant)
changes in $Y >> shift of Md curve
changes in interest rate >> mov't along curve
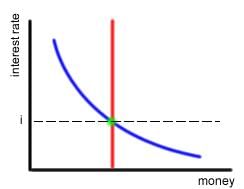
money supply (not dependent on interest rate at all)
money demand
equilibrium
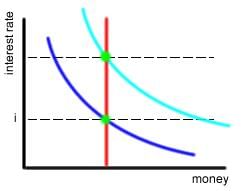
higher $Y >> higher interest rate
lower $Y >> lower interest rate
money demand always equals money supply at equilibrium, so interest rate adjusts
need higher interest rate w/ higher income to compel consumers to invest and have the same money demand as before, etc

|
Explore Courses for B Com exam
|

|
how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions?
Question Description
how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions? for B Com 2025 is part of B Com preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the B Com exam syllabus. Information about how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions? covers all topics & solutions for B Com 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions?.
how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions? for B Com 2025 is part of B Com preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the B Com exam syllabus. Information about how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions? covers all topics & solutions for B Com 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions?.
Solutions for how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for B Com.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for B Com Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions?, a detailed solution for how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions? has been provided alongside types of how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice how financial market achieve equilibrium Related: Equilibrium in Financial Markets - Financial Markets and Institutions? tests, examples and also practice B Com tests.

|
Explore Courses for B Com exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















