Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of &alph...
Start Learning for Free
Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by the formation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.
- a)Amylose
- b)Amylopectin
- c)Cellulose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in whi...
Glucose. It serves as a form of energy storage in animals, including humans. Glycogen is mainly stored in the liver and muscles, where it can be broken down into glucose when energy is needed.
The structure of glycogen is highly branched and consists of many glucose molecules linked together. It is formed through a process called glycogenesis, in which glucose molecules are added to existing glycogen chains.
Glycogen is an important energy source during periods of fasting or exercise when glucose levels in the body are low. It can be rapidly broken down into glucose through a process called glycogenolysis, which occurs mainly in the liver.
Glycogen also plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels. When blood glucose levels are high, insulin stimulates the liver to convert excess glucose into glycogen for storage. This helps to lower blood glucose levels. On the other hand, when blood glucose levels are low, glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen into glucose and release it into the bloodstream.
Overall, glycogen serves as an important energy reserve in the body and plays a crucial role in maintaining blood sugar levels.
The structure of glycogen is highly branched and consists of many glucose molecules linked together. It is formed through a process called glycogenesis, in which glucose molecules are added to existing glycogen chains.
Glycogen is an important energy source during periods of fasting or exercise when glucose levels in the body are low. It can be rapidly broken down into glucose through a process called glycogenolysis, which occurs mainly in the liver.
Glycogen also plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels. When blood glucose levels are high, insulin stimulates the liver to convert excess glucose into glycogen for storage. This helps to lower blood glucose levels. On the other hand, when blood glucose levels are low, glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen into glucose and release it into the bloodstream.
Overall, glycogen serves as an important energy reserve in the body and plays a crucial role in maintaining blood sugar levels.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in whi...
Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of αD glucose units in which chain is formed by C1−C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branchin occurs by the formation of C1−C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen can be shown below similar to the sturcture amplopectin.
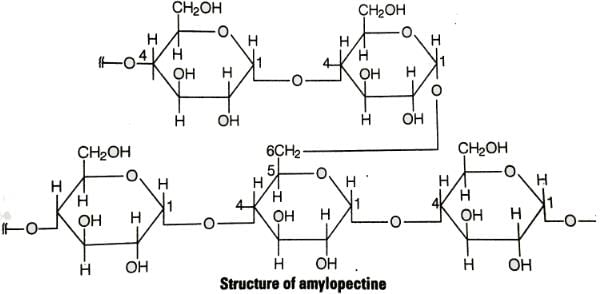


|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by theformation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.a)Amyloseb)Amylopectinc)Cellulosed)GlucoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















