Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Questions > Needed a Document for ruling the countryside ...
Start Learning for Free
Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map?
Verified Answer
Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: S...
Ans.
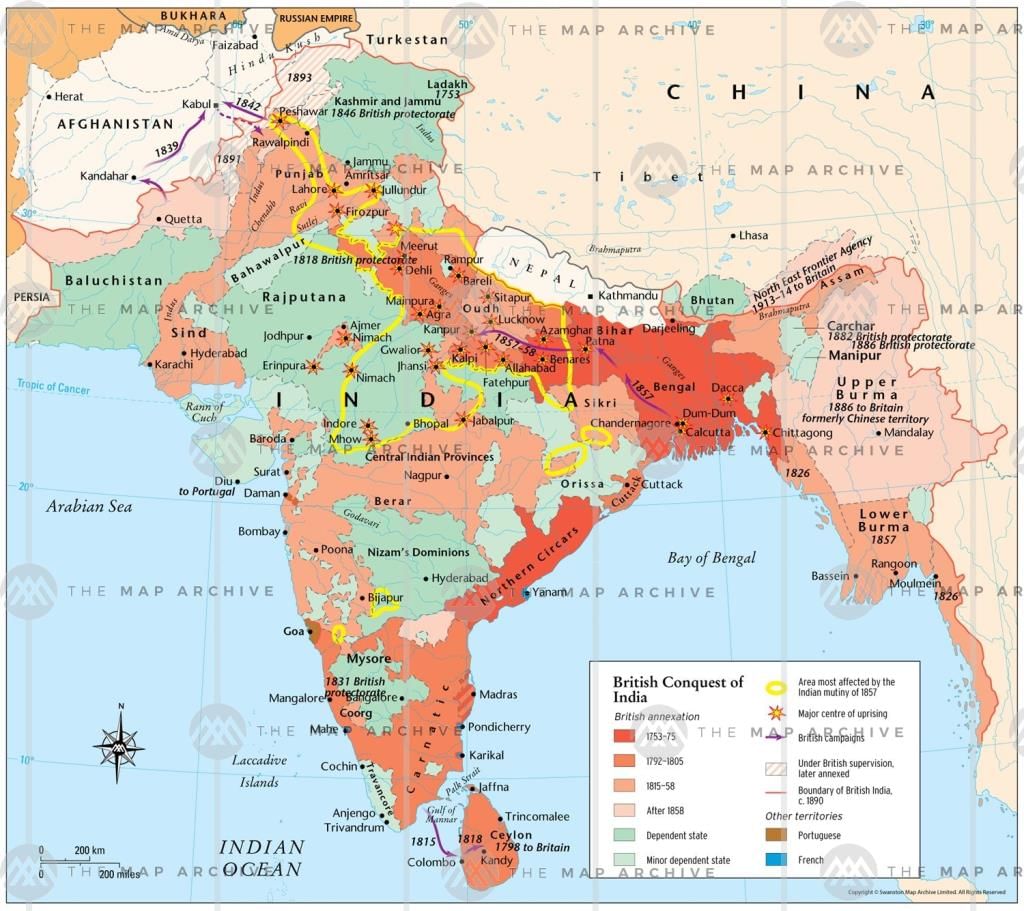
British Conquest of India 1753–1914
In 1600 the East India Company was established to run British trading operations in the Indian Ocean. It established numerous coastal trading posts and factories against competition from its Dutch, Portuguese and French counterparts. British influence was extended after victory against the Nawab of Bengal at the Battle of Plassey in 1757 and subsequent installation of a ruler under British control. Over the next century, the Company extended its rule both militarily (four wars with Mysore, three with the Marathas) and through coercive diplomacy: two-thirds of India was occupied by puppet rulers who retained titular power but accepted the Company’s suzerainty. Through subsidiary alliances, protection against other regional powers was provided in return for payment and nominal British control. This practice led to a widespread revolt against British rule; the Mutiny of 1857–58 saw the capture of Delhi, while the massacre of British civilians at Kanpur provoked a ruthless suppression, by the ‘army of retribution’. The Company, held responsible for these violent events, was replaced by the British colonial government, which took control of India through a network of local rulers under the British Raj. It became known as the Indian Empire in 1876, when Queen Victoria became Empress of India. The 'minor' provinces of Burma, which had come under British rule between 1824 and 1852, were consolidated into the 'major' province of Burma, following the Third Anglo-Burmese War and annexation of Upper Burma in 1885. In 1897 Burma became a Lieutenant-Governorship, with its capital at Rangoon.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 8 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 8 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: S...
Document for Ruling the Countryside Concept Map
- Title: Ruling the Countryside Concept Map
- Objective: To understand the key aspects of ruling the countryside in a structured format.
Key Components:
- Government: Highlight the role of the government in ruling the countryside, including governance structure, policies, and decision-making processes.
- Land Ownership: Explore the concept of land ownership and its implications on ruling the countryside, including land distribution, land rights, and land use regulations.
- Social Hierarchy: Discuss the social hierarchy in the countryside and how it influences power dynamics, relationships, and resource allocation.
- Economic Systems: Examine the economic systems in place in the countryside, such as agriculture, trade, and industry, and their impact on ruling strategies.
- Infrastructure: Analyze the infrastructure development in the countryside, including transportation, communication, and utilities, and their role in governance.
- Local Leadership: Explore the role of local leaders, such as village heads, in ruling the countryside and maintaining order and harmony.
Conclusion: By creating a concept map that visually represents the key components of ruling the countryside, students can gain a deeper understanding of the complex dynamics at play in rural governance. This document serves as a valuable tool for Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8 students to grasp the intricacies of ruling systems in rural areas.
- Title: Ruling the Countryside Concept Map
- Objective: To understand the key aspects of ruling the countryside in a structured format.
Key Components:
- Government: Highlight the role of the government in ruling the countryside, including governance structure, policies, and decision-making processes.
- Land Ownership: Explore the concept of land ownership and its implications on ruling the countryside, including land distribution, land rights, and land use regulations.
- Social Hierarchy: Discuss the social hierarchy in the countryside and how it influences power dynamics, relationships, and resource allocation.
- Economic Systems: Examine the economic systems in place in the countryside, such as agriculture, trade, and industry, and their impact on ruling strategies.
- Infrastructure: Analyze the infrastructure development in the countryside, including transportation, communication, and utilities, and their role in governance.
- Local Leadership: Explore the role of local leaders, such as village heads, in ruling the countryside and maintaining order and harmony.
Conclusion: By creating a concept map that visually represents the key components of ruling the countryside, students can gain a deeper understanding of the complex dynamics at play in rural governance. This document serves as a valuable tool for Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8 students to grasp the intricacies of ruling systems in rural areas.
Attention Class 8 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 8 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 8.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Similar Class 8 Doubts
Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8?
Question Description
Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8? for Class 8 2024 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8? covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8?.
Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8? for Class 8 2024 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8? covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8?.
Solutions for Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 8.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 8 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8?, a detailed solution for Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8? has been provided alongside types of Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Needed a Document for ruling the countryside concept map? Related: Social Science Studies (SST) for Class 8? tests, examples and also practice Class 8 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























