JEE Exam > JEE Questions > A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allo...
Start Learning for Free
A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is?
Verified Answer
A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly ...
Ans.
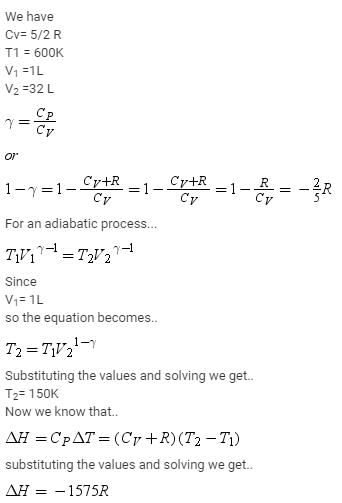
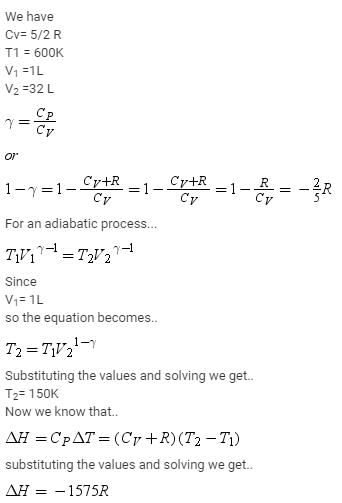
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
Most Upvoted Answer
A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly ...
Gas Expansion and Enthalpy Change
To determine the molar enthalpy change for the given gas expansion process, we need to consider the ideal gas behavior, reversible expansion, adiabatic conditions, and initial and final volumes.
Given Data:
- Cv,m = 5/2 R (specific heat capacity at constant volume)
- Initial volume (V1) = 1 litre
- Final volume (V2) = 32 litre
- Initial temperature (T1) = 327°C
Step 1: Conversion of Temperature to Kelvin Scale
The temperature needs to be converted from Celsius to Kelvin scale since the gas law equations require temperatures in Kelvin.
T1 (Kelvin) = T1 (°C) + 273.15
T1 (Kelvin) = 327 + 273.15 = 600.15 K
Step 2: Calculation of Molar Entropy Change
Since the process is adiabatic (no heat transfer), the change in entropy is zero (ΔS = 0).
Step 3: Calculation of ΔU (Change in Internal Energy)
In an adiabatic process, the change in internal energy (ΔU) is equal to the work done (W).
ΔU = W
For an ideal gas, the work done during an expansion process can be calculated using the formula:
W = (Cv,m * ΔT)
Where ΔT is the change in temperature.
Step 4: Calculation of ΔT (Change in Temperature)
The change in temperature can be calculated using the ideal gas law equation:
ΔT = (T2 - T1)
Where T2 is the final temperature, and T1 is the initial temperature.
Step 5: Calculation of T2 (Final Temperature)
Since the process is adiabatic, there is no heat transfer. Therefore, the final temperature (T2) can be calculated using the adiabatic expansion formula:
T2 * (V2/V1)^(γ-1) = T1
Where γ is the heat capacity ratio (Cp/Cv), which is equal to 5/2 for the given gas.
T2 = T1 / (V2/V1)^(γ-1)
Step 6: Calculation of ΔU (Change in Internal Energy)
Using the values of Cv,m, ΔT, and T2, we can now calculate the change in internal energy (ΔU).
ΔU = Cv,m * ΔT
Step 7: Calculation of ΔH (Change in Enthalpy)
Since the process is adiabatic, there is no heat transfer. Therefore, the change in enthalpy (ΔH) is equal to the change in internal energy (ΔU).
ΔH = ΔU
Step 8: Calculation of Molar Enthalpy Change
Finally, to calculate the molar enthalpy change, we divide the change in enthalpy (ΔH) by the number of moles (n) of the gas.
To determine the molar enthalpy change for the given gas expansion process, we need to consider the ideal gas behavior, reversible expansion, adiabatic conditions, and initial and final volumes.
Given Data:
- Cv,m = 5/2 R (specific heat capacity at constant volume)
- Initial volume (V1) = 1 litre
- Final volume (V2) = 32 litre
- Initial temperature (T1) = 327°C
Step 1: Conversion of Temperature to Kelvin Scale
The temperature needs to be converted from Celsius to Kelvin scale since the gas law equations require temperatures in Kelvin.
T1 (Kelvin) = T1 (°C) + 273.15
T1 (Kelvin) = 327 + 273.15 = 600.15 K
Step 2: Calculation of Molar Entropy Change
Since the process is adiabatic (no heat transfer), the change in entropy is zero (ΔS = 0).
Step 3: Calculation of ΔU (Change in Internal Energy)
In an adiabatic process, the change in internal energy (ΔU) is equal to the work done (W).
ΔU = W
For an ideal gas, the work done during an expansion process can be calculated using the formula:
W = (Cv,m * ΔT)
Where ΔT is the change in temperature.
Step 4: Calculation of ΔT (Change in Temperature)
The change in temperature can be calculated using the ideal gas law equation:
ΔT = (T2 - T1)
Where T2 is the final temperature, and T1 is the initial temperature.
Step 5: Calculation of T2 (Final Temperature)
Since the process is adiabatic, there is no heat transfer. Therefore, the final temperature (T2) can be calculated using the adiabatic expansion formula:
T2 * (V2/V1)^(γ-1) = T1
Where γ is the heat capacity ratio (Cp/Cv), which is equal to 5/2 for the given gas.
T2 = T1 / (V2/V1)^(γ-1)
Step 6: Calculation of ΔU (Change in Internal Energy)
Using the values of Cv,m, ΔT, and T2, we can now calculate the change in internal energy (ΔU).
ΔU = Cv,m * ΔT
Step 7: Calculation of ΔH (Change in Enthalpy)
Since the process is adiabatic, there is no heat transfer. Therefore, the change in enthalpy (ΔH) is equal to the change in internal energy (ΔU).
ΔH = ΔU
Step 8: Calculation of Molar Enthalpy Change
Finally, to calculate the molar enthalpy change, we divide the change in enthalpy (ΔH) by the number of moles (n) of the gas.
Community Answer
A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly ...


|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is?
Question Description
A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is?.
A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is?.
Solutions for A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is?, a detailed solution for A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is? has been provided alongside types of A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A gas (Cv,m= 5/2 R) behaving ideally was allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from 1 litre to 32 litre.It's initial temperature was 327 C .The molar enthalpy change for the process is? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























