Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Difference between diffusion and osmosis.?
Start Learning for Free
Difference between diffusion and osmosis.?
Verified Answer
Difference between diffusion and osmosis.?
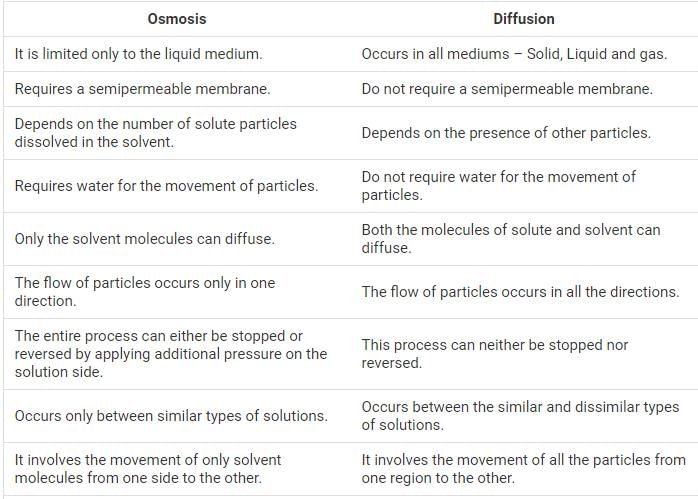
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Difference between diffusion and osmosis.?
DIFFUSION=It is the spontaneous movement of particles of a substance in a gas or liquid form from a region of its higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration.
FUNCTIONS
*It helps in exchange of respiratory gases.
*it helps in the distribution and spread of different substances in the cytoplasm.
OSMOSIS= the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane(plasma membrane) from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration.
FUNCTIONS
* roots absorb water from soil by osmosis.
* cell to cell movement of water absorbed by roots also takes place by osmosis.
FUNCTIONS
*It helps in exchange of respiratory gases.
*it helps in the distribution and spread of different substances in the cytoplasm.
OSMOSIS= the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane(plasma membrane) from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration.
FUNCTIONS
* roots absorb water from soil by osmosis.
* cell to cell movement of water absorbed by roots also takes place by osmosis.
Community Answer
Difference between diffusion and osmosis.?
Diffusion:
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. It occurs in both liquids and gases, as well as across cell membranes. Diffusion does not require any energy input and is driven by the random motion of molecules.
Key Points:
- Movement of molecules from high to low concentration
- Occurs in liquids, gases, and across cell membranes
- No energy input required
- Driven by random motion of molecules
Osmosis:
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. A semipermeable membrane allows the passage of water molecules but restricts the movement of solute particles. Osmosis occurs when there is a difference in solute concentration between two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane.
Key Points:
- Movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane
- Involves a difference in solute concentration
- Semipermeable membrane allows water passage but restricts solute movement
Differences:
1. Movement of Molecules:
- Diffusion: In diffusion, molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, regardless of the type of molecule.
- Osmosis: Osmosis specifically involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
2. Types of Membrane:
- Diffusion: Diffusion can occur in any type of membrane, including semipermeable membranes.
- Osmosis: Osmosis occurs across a semipermeable membrane, which allows the passage of water but restricts solute movement.
3. Concentration Gradient:
- Diffusion: The driving force behind diffusion is the concentration gradient, i.e., the difference in concentration between two regions.
- Osmosis: Osmosis occurs when there is a difference in solute concentration between two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane.
4. Energy Requirement:
- Diffusion: Diffusion is a passive process and does not require any energy input.
- Osmosis: Osmosis is also a passive process and does not require energy.
5. Examples:
- Diffusion: Examples of diffusion include the spreading of perfume in a room, the mixing of gases in the atmosphere, or the movement of molecules across a cell membrane.
- Osmosis: Examples of osmosis include the absorption of water by plant roots, the rehydration of dried fruits when placed in water, or the movement of water across red blood cells.
In conclusion, diffusion and osmosis are both passive processes involving the movement of molecules. Diffusion refers to the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, while osmosis specifically involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane in response to a difference in solute concentration.
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. It occurs in both liquids and gases, as well as across cell membranes. Diffusion does not require any energy input and is driven by the random motion of molecules.
Key Points:
- Movement of molecules from high to low concentration
- Occurs in liquids, gases, and across cell membranes
- No energy input required
- Driven by random motion of molecules
Osmosis:
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. A semipermeable membrane allows the passage of water molecules but restricts the movement of solute particles. Osmosis occurs when there is a difference in solute concentration between two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane.
Key Points:
- Movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane
- Involves a difference in solute concentration
- Semipermeable membrane allows water passage but restricts solute movement
Differences:
1. Movement of Molecules:
- Diffusion: In diffusion, molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, regardless of the type of molecule.
- Osmosis: Osmosis specifically involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
2. Types of Membrane:
- Diffusion: Diffusion can occur in any type of membrane, including semipermeable membranes.
- Osmosis: Osmosis occurs across a semipermeable membrane, which allows the passage of water but restricts solute movement.
3. Concentration Gradient:
- Diffusion: The driving force behind diffusion is the concentration gradient, i.e., the difference in concentration between two regions.
- Osmosis: Osmosis occurs when there is a difference in solute concentration between two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane.
4. Energy Requirement:
- Diffusion: Diffusion is a passive process and does not require any energy input.
- Osmosis: Osmosis is also a passive process and does not require energy.
5. Examples:
- Diffusion: Examples of diffusion include the spreading of perfume in a room, the mixing of gases in the atmosphere, or the movement of molecules across a cell membrane.
- Osmosis: Examples of osmosis include the absorption of water by plant roots, the rehydration of dried fruits when placed in water, or the movement of water across red blood cells.
In conclusion, diffusion and osmosis are both passive processes involving the movement of molecules. Diffusion refers to the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, while osmosis specifically involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane in response to a difference in solute concentration.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
Difference between diffusion and osmosis.?
Question Description
Difference between diffusion and osmosis.? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Difference between diffusion and osmosis.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference between diffusion and osmosis.?.
Difference between diffusion and osmosis.? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Difference between diffusion and osmosis.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference between diffusion and osmosis.?.
Solutions for Difference between diffusion and osmosis.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Difference between diffusion and osmosis.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Difference between diffusion and osmosis.?, a detailed solution for Difference between diffusion and osmosis.? has been provided alongside types of Difference between diffusion and osmosis.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Difference between diffusion and osmosis.? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























