Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > In an electronic circuit transistor is used f...
Start Learning for Free
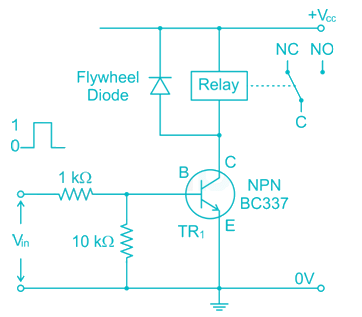
In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?
- a)A capacitor in series to the relay
- b)A resistor in series to the relay
- c)An inductor parallel to the relay
- d)A diode parallel to the relay
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a...
In transistor relay circuit when relay is in OFF state, high reverse voltage is developed across relay terminals, this can damage the transistor. Hence a diode is connected parallel to the relay, this clamps the voltage across the relay and helps dissipate the energy in diode.
Most Upvoted Answer
In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a...
Introduction:
In electronic circuits, transistors are commonly used for switching applications. However, when a transistor switches off a relay, a higher voltage can appear across the transistor, which can potentially damage the transistor. To protect the transistor from this voltage, a diode is typically used.
Explanation:
When a transistor switches off a relay, the coil of the relay generates a reverse voltage, also known as a back EMF (Electromotive Force). This back EMF can reach a high value and can damage the transistor if not properly controlled.
Function of the diode:
A diode connected in parallel to the relay provides a path for the back EMF to flow, protecting the transistor from the high voltage. When the transistor switches off, the diode becomes forward biased, allowing the back EMF to safely circulate through the diode rather than damaging the transistor.
Working principle:
When the transistor is switched on, it allows current to flow through the relay coil, energizing the relay. When the transistor switches off, the current flowing through the relay coil suddenly stops, leading to the generation of the back EMF.
Back EMF protection:
The diode, when connected in parallel to the relay, provides a low impedance path for the back EMF to circulate. The diode is typically connected with its anode connected to the positive terminal of the coil and its cathode connected to the negative terminal of the coil. This arrangement ensures that the back EMF flows through the diode, effectively clamping the voltage across the relay coil and protecting the transistor.
Diode characteristics:
When the diode is forward biased, it has a low resistance and allows current to flow through it. In this case, when the transistor switches off, the diode becomes forward biased and conducts the back EMF current. However, when the diode is reverse biased, it has a high resistance and blocks the flow of current.
Conclusion:
By connecting a diode in parallel to the relay in an electronic circuit, the transistor can be protected from the higher voltage that appears when the relay is switched off. The diode provides a low impedance path for the back EMF, preventing any damage to the transistor.
In electronic circuits, transistors are commonly used for switching applications. However, when a transistor switches off a relay, a higher voltage can appear across the transistor, which can potentially damage the transistor. To protect the transistor from this voltage, a diode is typically used.
Explanation:
When a transistor switches off a relay, the coil of the relay generates a reverse voltage, also known as a back EMF (Electromotive Force). This back EMF can reach a high value and can damage the transistor if not properly controlled.
Function of the diode:
A diode connected in parallel to the relay provides a path for the back EMF to flow, protecting the transistor from the high voltage. When the transistor switches off, the diode becomes forward biased, allowing the back EMF to safely circulate through the diode rather than damaging the transistor.
Working principle:
When the transistor is switched on, it allows current to flow through the relay coil, energizing the relay. When the transistor switches off, the current flowing through the relay coil suddenly stops, leading to the generation of the back EMF.
Back EMF protection:
The diode, when connected in parallel to the relay, provides a low impedance path for the back EMF to circulate. The diode is typically connected with its anode connected to the positive terminal of the coil and its cathode connected to the negative terminal of the coil. This arrangement ensures that the back EMF flows through the diode, effectively clamping the voltage across the relay coil and protecting the transistor.
Diode characteristics:
When the diode is forward biased, it has a low resistance and allows current to flow through it. In this case, when the transistor switches off, the diode becomes forward biased and conducts the back EMF current. However, when the diode is reverse biased, it has a high resistance and blocks the flow of current.
Conclusion:
By connecting a diode in parallel to the relay in an electronic circuit, the transistor can be protected from the higher voltage that appears when the relay is switched off. The diode provides a low impedance path for the back EMF, preventing any damage to the transistor.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In an electronic circuit transistor is used for switching ON and OFF a relay when the transistor switches OFF the relay a higher voltage appears across the transistor. How can a transistor be protected from this voltage?a)A capacitor in series to the relayb)A resistor in series to the relayc)An inductor parallel to the relayd)A diode parallel to the relayCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























