Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Which of the following reactions will not res...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?
- a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]
- b)Cannizaro reaction
- c)Wurtz reaction
- d)Friedel-Crafts acylation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of ca...
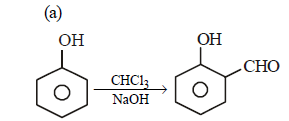
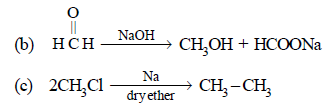
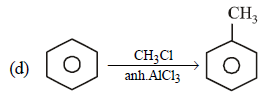
Note that new C–C bond is formed is a, c and d.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of ca...
Explanation of Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
When examining the reactions listed, it’s essential to identify which ones lead to the creation of carbon-carbon bonds.
Reimer-Tieman Reaction
- This reaction involves the ortho-formylation of phenols using chloroform and a strong base.
- It results in the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond in the product.
Cannizzaro Reaction
- In this reaction, aldehydes that lack alpha-hydrogens undergo disproportionation in the presence of a strong base.
- One molecule of the aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid, while another is reduced to an alcohol.
- Key Point: No new carbon-carbon bonds are formed; the carbon skeleton remains unchanged.
Wurtz Reaction
- This reaction involves the coupling of alkyl halides in the presence of sodium metal, leading to the formation of alkanes.
- New carbon-carbon bonds are indeed formed, making this reaction a key method for building larger hydrocarbons.
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
- This reaction introduces an acyl group into an aromatic ring using an acyl chloride and a Lewis acid.
- Although it results in a new carbon atom being added to the aromatic system, it does not create a new carbon-carbon bond between two distinct carbon chains.
Conclusion
- The Cannizzaro reaction is unique among the options as it does not facilitate the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds. Instead, it rearranges existing carbon atoms without any coupling or elongation of the carbon chain.
When examining the reactions listed, it’s essential to identify which ones lead to the creation of carbon-carbon bonds.
Reimer-Tieman Reaction
- This reaction involves the ortho-formylation of phenols using chloroform and a strong base.
- It results in the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond in the product.
Cannizzaro Reaction
- In this reaction, aldehydes that lack alpha-hydrogens undergo disproportionation in the presence of a strong base.
- One molecule of the aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid, while another is reduced to an alcohol.
- Key Point: No new carbon-carbon bonds are formed; the carbon skeleton remains unchanged.
Wurtz Reaction
- This reaction involves the coupling of alkyl halides in the presence of sodium metal, leading to the formation of alkanes.
- New carbon-carbon bonds are indeed formed, making this reaction a key method for building larger hydrocarbons.
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
- This reaction introduces an acyl group into an aromatic ring using an acyl chloride and a Lewis acid.
- Although it results in a new carbon atom being added to the aromatic system, it does not create a new carbon-carbon bond between two distinct carbon chains.
Conclusion
- The Cannizzaro reaction is unique among the options as it does not facilitate the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds. Instead, it rearranges existing carbon atoms without any coupling or elongation of the carbon chain.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]b)Cannizaro reactionc)Wurtz reactiond)Friedel-Crafts acylationCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























