Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be...
Start Learning for Free
n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?
- a)PCl5 [2002]
- b)Reduction
- c)Oxidation with potassium dichromate
- d)Ozonolysis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished...
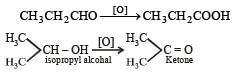
Primary alcohol on oxidation give aldehyde which on further oxidation give carboxylic acid whereas secondary alcohols give ketone.
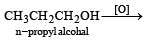
Most Upvoted Answer
n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished...
Chemical Distinguishing of n-Propyl Alcohol and Isopropyl Alcohol
Oxidation with Potassium Dichromate
When n-propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol are treated with potassium dichromate, they undergo oxidation reactions at different rates due to their different structures. Isopropyl alcohol will oxidize faster than n-propyl alcohol because of the presence of a secondary alcohol group in isopropyl alcohol compared to the primary alcohol group in n-propyl alcohol.
Reaction Mechanism
- Isopropyl alcohol will be oxidized to acetone by potassium dichromate, while n-propyl alcohol will be oxidized to propanal.
- The oxidation of isopropyl alcohol to acetone involves the loss of a hydrogen atom from the secondary alcohol group, forming a ketone.
- The oxidation of n-propyl alcohol to propanal involves the loss of a hydrogen atom from the primary alcohol group, forming an aldehyde.
Observation
- By observing the products formed after oxidation with potassium dichromate, it is possible to distinguish between n-propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol based on the different functional groups present in the final products.
- Isopropyl alcohol will give acetone as the main product, while n-propyl alcohol will give propanal as the main product.
Therefore, oxidation with potassium dichromate can be used as a reagent to chemically distinguish between n-propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol based on their different reaction rates and products formed.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?a)PCl5 [2002]b)Reductionc)Oxidation with potassium dichromated)OzonolysisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















