Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Which of the following is least reactive in a...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]
- a)(CH3)3 C - Cl
- b)CH2 = CHCl
- c)CH3CH2Cl
- d)CH2 = CHCH2 Cl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitutio...
H2C = CHCl is capable of showing resonance which develops a partial double bond, character to C–Cl bond, thereby making it less reactive toward nucleophilic substitution. ..
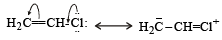
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitutio...
Reactivity in nucleophilic substitution reactions is determined by the strength of the bond between the carbon and the leaving group. The weaker the bond, the more reactive the compound will be. In this case, we have four compounds to compare:
a) (CH3)3C-Cl
b) CH2=CHCl
c) CH3CH2Cl
d) CH2=CHCH2Cl
To determine the reactivity, we need to consider the nature of the leaving group and the stability of the carbocation intermediate formed during the reaction.
1. Leaving Group:
The leaving group in all four compounds is a chloride ion (Cl-). Chloride ions are good leaving groups because they are stable and can easily accept a pair of electrons. Therefore, the nature of the leaving group does not determine the reactivity in this case.
2. Carbocation Stability:
The more stable the carbocation intermediate, the more reactive the compound. Carbocation stability depends on the number of alkyl groups attached to the positively charged carbon atom. The order of carbocation stability is as follows:
tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl
a) (CH3)3C-Cl: This compound forms a tertiary carbocation, which is the most stable carbocation. Therefore, it is the most reactive compound.
c) CH3CH2Cl: This compound forms a primary carbocation, which is less stable than a tertiary carbocation. Therefore, it is less reactive than compound (a).
d) CH2=CHCH2Cl: This compound forms a secondary carbocation, which is more stable than a primary carbocation but less stable than a tertiary carbocation. Therefore, it is less reactive than compound (a) but more reactive than compound (c).
b) CH2=CHCl: This compound does not form a carbocation intermediate during the reaction. Instead, it undergoes a concerted mechanism called an SN2 reaction, where the nucleophile attacks the carbon atom and the leaving group leaves simultaneously. This mechanism does not involve the formation of a carbocation intermediate. Therefore, compound (b) is the least reactive among the four compounds.
In summary, compound (b) (CH2=CHCl) is the least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution reaction because it does not undergo carbocation formation and follows an SN2 mechanism.
a) (CH3)3C-Cl
b) CH2=CHCl
c) CH3CH2Cl
d) CH2=CHCH2Cl
To determine the reactivity, we need to consider the nature of the leaving group and the stability of the carbocation intermediate formed during the reaction.
1. Leaving Group:
The leaving group in all four compounds is a chloride ion (Cl-). Chloride ions are good leaving groups because they are stable and can easily accept a pair of electrons. Therefore, the nature of the leaving group does not determine the reactivity in this case.
2. Carbocation Stability:
The more stable the carbocation intermediate, the more reactive the compound. Carbocation stability depends on the number of alkyl groups attached to the positively charged carbon atom. The order of carbocation stability is as follows:
tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl
a) (CH3)3C-Cl: This compound forms a tertiary carbocation, which is the most stable carbocation. Therefore, it is the most reactive compound.
c) CH3CH2Cl: This compound forms a primary carbocation, which is less stable than a tertiary carbocation. Therefore, it is less reactive than compound (a).
d) CH2=CHCH2Cl: This compound forms a secondary carbocation, which is more stable than a primary carbocation but less stable than a tertiary carbocation. Therefore, it is less reactive than compound (a) but more reactive than compound (c).
b) CH2=CHCl: This compound does not form a carbocation intermediate during the reaction. Instead, it undergoes a concerted mechanism called an SN2 reaction, where the nucleophile attacks the carbon atom and the leaving group leaves simultaneously. This mechanism does not involve the formation of a carbocation intermediate. Therefore, compound (b) is the least reactive among the four compounds.
In summary, compound (b) (CH2=CHCl) is the least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution reaction because it does not undergo carbocation formation and follows an SN2 mechanism.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Question Description
Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution r eaction. [2004]a)(CH3)3 C - Clb)CH2 = CHClc)CH3CH2Cld)CH2 = CHCH2 ClCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















