Railways Exam > Railways Questions > When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less t...
Start Learning for Free
When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called as
- a)Inversion Lapse rate
- b)Super-Adiabatic Lapse rate
- c)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rate
- d)Negative Lapse rate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lap...
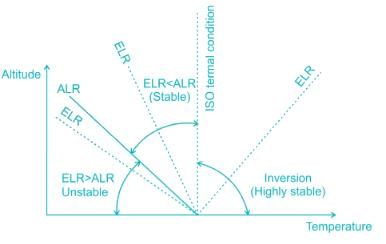
When
ELR > ALR – Superadiabatic lapse rate – Unstable Environment
ELR < ALR – Sub – adiabatic lapse rate – Stable Environment
ELR = ALR – Neutral Condition
ELR is negative – Inversion
Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is - 9.8oC per 1000 m rise
ELR > ALR – Superadiabatic lapse rate – Unstable Environment
ELR < ALR – Sub – adiabatic lapse rate – Stable Environment
ELR = ALR – Neutral Condition
ELR is negative – Inversion
Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is - 9.8oC per 1000 m rise
Most Upvoted Answer
When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lap...
Explanation:
The adiabatic lapse rate (ALR) refers to the rate at which the temperature of a parcel of air changes as it rises or sinks in the atmosphere without exchanging heat with its surroundings. It is influenced by the compression or expansion of the air parcel.
The environmental lapse rate (ELR) refers to the actual rate at which the temperature of the surrounding atmosphere changes with altitude. It is influenced by various factors such as solar radiation, convection, and advection.
When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), it means that the temperature of the surrounding atmosphere is decreasing at a faster rate with altitude compared to the temperature change of the rising or sinking air parcel.
Implications:
This condition has several implications for the atmosphere and weather conditions:
1. Super-Adiabatic Lapse Rate: When the ALR is less than the ELR, the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called a super-adiabatic lapse rate. This implies that the air parcel is cooler than its surroundings as it rises or warmer than its surroundings as it sinks. This condition is associated with unstable atmospheric conditions.
2. Instability: The super-adiabatic lapse rate indicates that the air parcel will continue to rise if it is already ascending, or continue to sink if it is already descending, without being influenced by its surrounding environment. This promotes vertical motion and can lead to the development of clouds, thunderstorms, and other forms of severe weather.
3. Convection: The super-adiabatic lapse rate is favorable for the development of convection. As the air parcel rises, it cools at a slower rate compared to its surroundings, leading to buoyancy and the formation of updrafts. These updrafts can fuel the growth of cumulus clouds and thunderstorms.
4. Vertical Mixing: The super-adiabatic lapse rate promotes vertical mixing of air, allowing for the exchange of heat, moisture, and pollutants between different layers of the atmosphere. This can have implications for air quality, as pollutants can be transported vertically and horizontally.
In summary, when the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called a super-adiabatic lapse rate. This condition is associated with unstable atmospheric conditions, convection, and the potential for the development of severe weather.
The adiabatic lapse rate (ALR) refers to the rate at which the temperature of a parcel of air changes as it rises or sinks in the atmosphere without exchanging heat with its surroundings. It is influenced by the compression or expansion of the air parcel.
The environmental lapse rate (ELR) refers to the actual rate at which the temperature of the surrounding atmosphere changes with altitude. It is influenced by various factors such as solar radiation, convection, and advection.
When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), it means that the temperature of the surrounding atmosphere is decreasing at a faster rate with altitude compared to the temperature change of the rising or sinking air parcel.
Implications:
This condition has several implications for the atmosphere and weather conditions:
1. Super-Adiabatic Lapse Rate: When the ALR is less than the ELR, the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called a super-adiabatic lapse rate. This implies that the air parcel is cooler than its surroundings as it rises or warmer than its surroundings as it sinks. This condition is associated with unstable atmospheric conditions.
2. Instability: The super-adiabatic lapse rate indicates that the air parcel will continue to rise if it is already ascending, or continue to sink if it is already descending, without being influenced by its surrounding environment. This promotes vertical motion and can lead to the development of clouds, thunderstorms, and other forms of severe weather.
3. Convection: The super-adiabatic lapse rate is favorable for the development of convection. As the air parcel rises, it cools at a slower rate compared to its surroundings, leading to buoyancy and the formation of updrafts. These updrafts can fuel the growth of cumulus clouds and thunderstorms.
4. Vertical Mixing: The super-adiabatic lapse rate promotes vertical mixing of air, allowing for the exchange of heat, moisture, and pollutants between different layers of the atmosphere. This can have implications for air quality, as pollutants can be transported vertically and horizontally.
In summary, when the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called a super-adiabatic lapse rate. This condition is associated with unstable atmospheric conditions, convection, and the potential for the development of severe weather.
Attention Railways Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Railways study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Railways.

|
Explore Courses for Railways exam
|

|
Similar Railways Doubts
When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Railways 2024 is part of Railways preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Railways exam syllabus. Information about When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Railways 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Railways 2024 is part of Railways preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Railways exam syllabus. Information about When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Railways 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Railways.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Railways Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice When the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR) is less than the Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR), then the prevailing environmental lapse rate is called asa)Inversion Lapse rateb)Super-Adiabatic Lapse ratec)Sub-Adiabatic Lapse rated)Negative Lapse rateCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Railways tests.

|
Explore Courses for Railways exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























