Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > In the engineering stress-strain curve for mi...
Start Learning for Free
In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers to
- a)Yield stress
- b)Proportional limit
- c)Maximum stress
- d)Fracture stress
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Te...
The engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel is
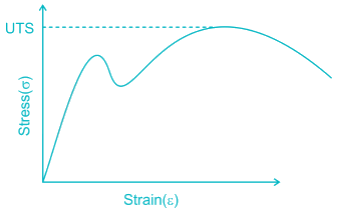
Ultimate tensile strength represents the maximum stress that a material can withstand without Fracture.

Ultimate tensile strength represents the maximum stress that a material can withstand without Fracture.
Most Upvoted Answer
In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Te...
Yes the correct answer is C
Ultimate tensile strength or simply, tensile strength, is the measure of the maximum stress that an object/material/structure can withstand without being elongated, stretched or pulled.Tensile properties of a material indicate how it will react to forces app
lied on it in tension. As you can imagine, some materials break when a great deal of force is applied to them, while others get elongated or physically deformed in some other way. Materials that break very sharply are said to undergo a ‘brittle failure’.
On the other hand, there are some materials that can handle/withstand a great deal of stress while being pulled or stretched before breaking. The term ‘ultimate tensile strength’ (or UTS) is used to refer to the maximum stress that a material can handle before becoming elongated, stretched or pulled.
As you can se from the stress-strain diagram as the stresses reached UTS point It have the maximum stress. Hence for a tensile material UTS is the failure stress .Once the tensile material is entertained with UTS the material is failed.
Ultimate tensile strength or simply, tensile strength, is the measure of the maximum stress that an object/material/structure can withstand without being elongated, stretched or pulled.Tensile properties of a material indicate how it will react to forces app
lied on it in tension. As you can imagine, some materials break when a great deal of force is applied to them, while others get elongated or physically deformed in some other way. Materials that break very sharply are said to undergo a ‘brittle failure’.
On the other hand, there are some materials that can handle/withstand a great deal of stress while being pulled or stretched before breaking. The term ‘ultimate tensile strength’ (or UTS) is used to refer to the maximum stress that a material can handle before becoming elongated, stretched or pulled.
As you can se from the stress-strain diagram as the stresses reached UTS point It have the maximum stress. Hence for a tensile material UTS is the failure stress .Once the tensile material is entertained with UTS the material is failed.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Te...
The Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) in the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel refers to the maximum stress that the material can withstand before it breaks or fractures.
Explanation:
The engineering stress-strain curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between stress and strain during the tensile testing of a material. It helps in understanding the mechanical properties of the material, such as its strength, ductility, and toughness.
Key Definitions:
Before explaining the UTS, let's define some key terms related to the stress-strain curve:
1. Yield Stress: Yield stress is the point on the stress-strain curve where the material starts to deform plastically (permanently) after the elastic deformation. It represents the onset of plastic deformation and is an important parameter for determining the material's strength.
2. Proportional Limit: Proportional limit is the point on the stress-strain curve up to which the stress and strain remain directly proportional. Beyond this point, the material undergoes non-linear deformation and does not exhibit elastic behavior.
3. Maximum Stress: Maximum stress is the highest point on the stress-strain curve, which indicates the maximum stress the material experienced during the test. This point may or may not coincide with the UTS depending on the material's behavior.
4. Fracture Stress: Fracture stress is the stress at which the material fractures or breaks. It is the point where the material cannot withstand any further stress and fails.
Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS):
The UTS refers to the maximum stress that a material can sustain before it breaks or fractures. It is the highest point on the stress-strain curve and is an important parameter for determining the material's strength. The UTS value indicates the material's ability to resist external forces or loads without experiencing failure.
In the case of mild steel, the UTS is typically around 400-550 MPa (MegaPascals). This means that mild steel can withstand stress up to this value before it fractures. It is an important parameter for design and structural analysis as it helps in determining the maximum load a structure or component can bear before failure.
It is important to note that UTS is not necessarily the same as the yield stress or proportional limit. In some materials, the UTS may occur after the yield stress or proportional limit, indicating that the material undergoes significant plastic deformation before fracturing. In other cases, the UTS may coincide with the yield stress or proportional limit, suggesting that the material fractures without undergoing significant plastic deformation.
In conclusion, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) in the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel refers to the maximum stress the material can withstand before it breaks or fractures. It is an important parameter for assessing the material's strength and its ability to resist external loads.
Explanation:
The engineering stress-strain curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between stress and strain during the tensile testing of a material. It helps in understanding the mechanical properties of the material, such as its strength, ductility, and toughness.
Key Definitions:
Before explaining the UTS, let's define some key terms related to the stress-strain curve:
1. Yield Stress: Yield stress is the point on the stress-strain curve where the material starts to deform plastically (permanently) after the elastic deformation. It represents the onset of plastic deformation and is an important parameter for determining the material's strength.
2. Proportional Limit: Proportional limit is the point on the stress-strain curve up to which the stress and strain remain directly proportional. Beyond this point, the material undergoes non-linear deformation and does not exhibit elastic behavior.
3. Maximum Stress: Maximum stress is the highest point on the stress-strain curve, which indicates the maximum stress the material experienced during the test. This point may or may not coincide with the UTS depending on the material's behavior.
4. Fracture Stress: Fracture stress is the stress at which the material fractures or breaks. It is the point where the material cannot withstand any further stress and fails.
Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS):
The UTS refers to the maximum stress that a material can sustain before it breaks or fractures. It is the highest point on the stress-strain curve and is an important parameter for determining the material's strength. The UTS value indicates the material's ability to resist external forces or loads without experiencing failure.
In the case of mild steel, the UTS is typically around 400-550 MPa (MegaPascals). This means that mild steel can withstand stress up to this value before it fractures. It is an important parameter for design and structural analysis as it helps in determining the maximum load a structure or component can bear before failure.
It is important to note that UTS is not necessarily the same as the yield stress or proportional limit. In some materials, the UTS may occur after the yield stress or proportional limit, indicating that the material undergoes significant plastic deformation before fracturing. In other cases, the UTS may coincide with the yield stress or proportional limit, suggesting that the material fractures without undergoing significant plastic deformation.
In conclusion, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) in the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel refers to the maximum stress the material can withstand before it breaks or fractures. It is an important parameter for assessing the material's strength and its ability to resist external loads.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In the engineering stress-strain curve for mild steel, the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) refers toa)Yield stressb)Proportional limitc)Maximum stressd)Fracture stressCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















