Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > What is the difference between inertia and mo...
Start Learning for Free
What is the difference between inertia and momentum?
Verified Answer
What is the difference between inertia and momentum?
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the difference between inertia and momentum?
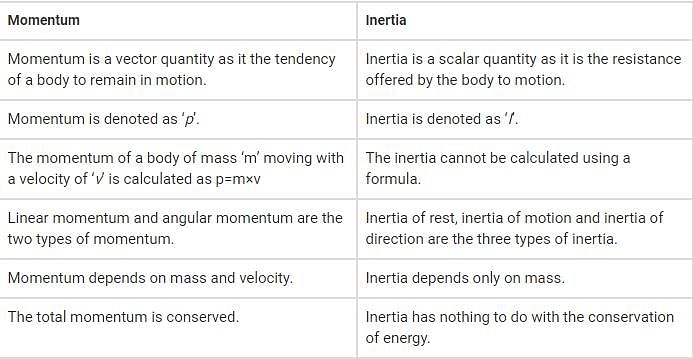
The tendency of a body to remain at rest or if it is moving to continue moving is called inertia whereas momentum is the product of mass and velocity.
Community Answer
What is the difference between inertia and momentum?
Inertia:
Inertia refers to the property of an object to resist any change in its state of motion, whether it is at rest or in motion. It is a fundamental concept in physics and is closely related to the mass of an object. Inertia can be thought of as a measure of how difficult it is to change an object's velocity. The more massive an object is, the greater its inertia and the more force is required to accelerate or decelerate it.
Momentum:
Momentum, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that describes the motion of an object. It is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity. Momentum depends on both the mass and the velocity of an object, which means that two objects with the same mass can have different momenta if they are moving at different velocities.
Differences:
There are several key differences between inertia and momentum:
Definition:
- Inertia is the property of an object to resist changes in its state of motion.
- Momentum is a measure of an object's motion and is calculated as the product of its mass and velocity.
Quantities:
- Inertia is a scalar quantity and is directly related to an object's mass.
- Momentum is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude and direction.
Change in Motion:
- Inertia describes an object's resistance to changes in its state of motion.
- Momentum describes an object's motion and how difficult it is to change that motion.
Relation to Mass:
- Inertia is directly proportional to an object's mass. The greater the mass, the greater the inertia.
- Momentum is also directly proportional to an object's mass. Increasing the mass increases the momentum.
Relation to Velocity:
- Inertia does not depend on an object's velocity. It only depends on its mass.
- Momentum depends on both an object's mass and its velocity. Increasing the velocity increases the momentum.
Implications:
- Inertia is responsible for objects staying at rest or continuing to move in a straight line at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
- Momentum is involved in collisions and interactions between objects. It determines how objects will move and react to forces.
In summary, inertia is a property of an object that resists changes in its motion, while momentum describes the motion of an object. Inertia depends only on an object's mass, while momentum depends on both mass and velocity.
Inertia refers to the property of an object to resist any change in its state of motion, whether it is at rest or in motion. It is a fundamental concept in physics and is closely related to the mass of an object. Inertia can be thought of as a measure of how difficult it is to change an object's velocity. The more massive an object is, the greater its inertia and the more force is required to accelerate or decelerate it.
Momentum:
Momentum, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that describes the motion of an object. It is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity. Momentum depends on both the mass and the velocity of an object, which means that two objects with the same mass can have different momenta if they are moving at different velocities.
Differences:
There are several key differences between inertia and momentum:
Definition:
- Inertia is the property of an object to resist changes in its state of motion.
- Momentum is a measure of an object's motion and is calculated as the product of its mass and velocity.
Quantities:
- Inertia is a scalar quantity and is directly related to an object's mass.
- Momentum is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude and direction.
Change in Motion:
- Inertia describes an object's resistance to changes in its state of motion.
- Momentum describes an object's motion and how difficult it is to change that motion.
Relation to Mass:
- Inertia is directly proportional to an object's mass. The greater the mass, the greater the inertia.
- Momentum is also directly proportional to an object's mass. Increasing the mass increases the momentum.
Relation to Velocity:
- Inertia does not depend on an object's velocity. It only depends on its mass.
- Momentum depends on both an object's mass and its velocity. Increasing the velocity increases the momentum.
Implications:
- Inertia is responsible for objects staying at rest or continuing to move in a straight line at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
- Momentum is involved in collisions and interactions between objects. It determines how objects will move and react to forces.
In summary, inertia is a property of an object that resists changes in its motion, while momentum describes the motion of an object. Inertia depends only on an object's mass, while momentum depends on both mass and velocity.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
What is the difference between inertia and momentum?
Question Description
What is the difference between inertia and momentum? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between inertia and momentum? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between inertia and momentum?.
What is the difference between inertia and momentum? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between inertia and momentum? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between inertia and momentum?.
Solutions for What is the difference between inertia and momentum? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the difference between inertia and momentum? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the difference between inertia and momentum?, a detailed solution for What is the difference between inertia and momentum? has been provided alongside types of What is the difference between inertia and momentum? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the difference between inertia and momentum? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























