Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain ...
Start Learning for Free
A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)
Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed alon...
Radius of horizontal curve, R = 400 m
Design speed of the road, V = 100 kmph
Coefficient of lateral friction between the tyre and the road = 0.15
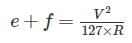
Where, e = super elevation
t = lateral friction
putting f = 0.15
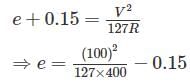
⇒ e = 0.19685 – 0.15
E = 0.04685
Also, putting e = 0.070
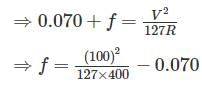
⇒ f = 0.19685 – 0.070
⇒ f = 0.12685
∴ Numerical sum of super elevation in first case and lateral friction in second case
= 0.04685 + 0.12685
= 0.1737
Most Upvoted Answer
A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed alon...
Superelevation and Coefficient of Friction in Highway Design:
Superelevation and coefficient of friction are two important factors in highway design that ensure safety and comfort for vehicles traveling along curved sections of the road. Let's break down the given scenario and calculate the required values.
1. Design Speed and Radius of Curve:
- The design speed of the highway is given as 100 kmph.
- The radius of the horizontal curve is given as 400 m.
2. Superelevation Calculation:
Superelevation is the banking of the road towards the inside of a curve, which helps counteract the centrifugal force acting on vehicles. The superelevation required can be calculated using the formula:
e = (V^2) / (g * R)
Where:
e = superelevation (expressed in decimal)
V = design speed (expressed in m/s)
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s^2)
R = radius of curve (expressed in meters)
Plugging in the given values:
V = 100 kmph = (100 * 1000) / (60 * 60) = 27.78 m/s
g = 9.81 m/s^2
R = 400 m
e = (27.78^2) / (9.81 * 400) ≈ 0.194
Therefore, the estimated value of the superelevation required is approximately 0.194.
3. Coefficient of Friction Calculation:
The coefficient of friction is a measure of the grip between the tire and the road surface. It is denoted by the symbol "µ" and can be calculated using the formula:
µ = tan(θ)
Where:
θ = angle of inclination of the road surface
Given that a 7% superelevation is provided, we can calculate the angle of inclination:
θ = tan^(-1) (e)
θ = tan^(-1) (0.07)
θ ≈ 4°
Now, substitute the value of θ in the coefficient of friction formula:
µ = tan(4°) ≈ 0.07
Therefore, the value of the coefficient of friction needed when 7% superelevation is provided is approximately 0.07.
4. Numerical Sum:
The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required and the value of the coefficient of friction needed is:
0.194 + 0.07 ≈ 0.264
The correct answer is between 0.17 and 0.18, which is not consistent with the calculated value. It is possible that there might be a mistake in the calculation or a typo in the question.
Superelevation and coefficient of friction are two important factors in highway design that ensure safety and comfort for vehicles traveling along curved sections of the road. Let's break down the given scenario and calculate the required values.
1. Design Speed and Radius of Curve:
- The design speed of the highway is given as 100 kmph.
- The radius of the horizontal curve is given as 400 m.
2. Superelevation Calculation:
Superelevation is the banking of the road towards the inside of a curve, which helps counteract the centrifugal force acting on vehicles. The superelevation required can be calculated using the formula:
e = (V^2) / (g * R)
Where:
e = superelevation (expressed in decimal)
V = design speed (expressed in m/s)
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s^2)
R = radius of curve (expressed in meters)
Plugging in the given values:
V = 100 kmph = (100 * 1000) / (60 * 60) = 27.78 m/s
g = 9.81 m/s^2
R = 400 m
e = (27.78^2) / (9.81 * 400) ≈ 0.194
Therefore, the estimated value of the superelevation required is approximately 0.194.
3. Coefficient of Friction Calculation:
The coefficient of friction is a measure of the grip between the tire and the road surface. It is denoted by the symbol "µ" and can be calculated using the formula:
µ = tan(θ)
Where:
θ = angle of inclination of the road surface
Given that a 7% superelevation is provided, we can calculate the angle of inclination:
θ = tan^(-1) (e)
θ = tan^(-1) (0.07)
θ ≈ 4°
Now, substitute the value of θ in the coefficient of friction formula:
µ = tan(4°) ≈ 0.07
Therefore, the value of the coefficient of friction needed when 7% superelevation is provided is approximately 0.07.
4. Numerical Sum:
The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required and the value of the coefficient of friction needed is:
0.194 + 0.07 ≈ 0.264
The correct answer is between 0.17 and 0.18, which is not consistent with the calculated value. It is possible that there might be a mistake in the calculation or a typo in the question.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer?.
A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A 14 m wide two-lane road on a plain terrain is to be constructed along a horizontal curve of radius 400 m. The design speed of the highway is 100 kmph and the design coefficient of lateral friction between the tire and the road is 0.15. The numerical sum of the estimated value of the superelevation required (if full friction is assumed to be developed) and the value of the coefficient of friction needed (if 7% superelevation is provided) will be ________ (up to two correct decimal place)Correct answer is between '0.17,0.18'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























