Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethy...
Start Learning for Free
Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]
- a)LiAlH4
- b)Zn-Hg/HCl
- c)NaBH4
- d)CH3MgI
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by wh...
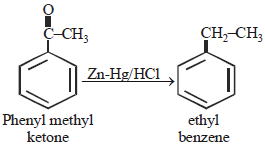
This reaction is known as clemmensen's
reduction.
reduction.
Most Upvoted Answer
Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by wh...
Conversion of Phenylmethyl ketone to Ethylbenzene
Introduction:
Phenylmethyl ketone, also known as acetophenone, can be converted into ethylbenzene through a one-step reaction using specific reagents. This conversion involves reducing the carbonyl group of the ketone to an alcohol and then further reducing it to a hydrocarbon.
Reagents:
The correct reagent for this one-step conversion is option 'B', which is Zn-Hg/HCl.
Explanation:
The Zn-Hg/HCl reagent is commonly referred to as Clemmensen reduction. It is a powerful reducing agent that is capable of converting carbonyl groups (such as ketones) into hydrocarbons.
Reaction mechanism:
The conversion of phenylmethyl ketone to ethylbenzene using Zn-Hg/HCl reagent can be explained through the following reaction mechanism:
1. Deprotonation:
The Zn-Hg/HCl reagent serves as a source of H- ions. In the presence of acidic conditions (HCl), the H- ions are generated, which can abstract a proton from the ketone.
2. Formation of carbanion:
The deprotonation of the ketone leads to the formation of a carbanion intermediate. This carbanion is stabilized by resonance with the aromatic ring.
3. Addition of Zn-Hg:
The carbanion intermediate then adds to the Zn-Hg, forming a new carbon-carbon bond. This step results in the formation of an alkyl zinc intermediate.
4. Acidic workup:
The alkyl zinc intermediate is then treated with an acidic workup, which involves the addition of HCl. This acidic environment helps in the removal of the zinc atom and the formation of the desired product, ethylbenzene.
Overall reaction:
The overall reaction can be summarized as follows:
Phenylmethyl ketone + Zn-Hg/HCl → Ethylbenzene
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the conversion of phenylmethyl ketone to ethylbenzene can be achieved in one step using Zn-Hg/HCl reagent. This reagent acts as a powerful reducing agent, allowing for the transformation of the carbonyl group into a hydrocarbon.
Introduction:
Phenylmethyl ketone, also known as acetophenone, can be converted into ethylbenzene through a one-step reaction using specific reagents. This conversion involves reducing the carbonyl group of the ketone to an alcohol and then further reducing it to a hydrocarbon.
Reagents:
The correct reagent for this one-step conversion is option 'B', which is Zn-Hg/HCl.
Explanation:
The Zn-Hg/HCl reagent is commonly referred to as Clemmensen reduction. It is a powerful reducing agent that is capable of converting carbonyl groups (such as ketones) into hydrocarbons.
Reaction mechanism:
The conversion of phenylmethyl ketone to ethylbenzene using Zn-Hg/HCl reagent can be explained through the following reaction mechanism:
1. Deprotonation:
The Zn-Hg/HCl reagent serves as a source of H- ions. In the presence of acidic conditions (HCl), the H- ions are generated, which can abstract a proton from the ketone.
2. Formation of carbanion:
The deprotonation of the ketone leads to the formation of a carbanion intermediate. This carbanion is stabilized by resonance with the aromatic ring.
3. Addition of Zn-Hg:
The carbanion intermediate then adds to the Zn-Hg, forming a new carbon-carbon bond. This step results in the formation of an alkyl zinc intermediate.
4. Acidic workup:
The alkyl zinc intermediate is then treated with an acidic workup, which involves the addition of HCl. This acidic environment helps in the removal of the zinc atom and the formation of the desired product, ethylbenzene.
Overall reaction:
The overall reaction can be summarized as follows:
Phenylmethyl ketone + Zn-Hg/HCl → Ethylbenzene
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the conversion of phenylmethyl ketone to ethylbenzene can be achieved in one step using Zn-Hg/HCl reagent. This reagent acts as a powerful reducing agent, allowing for the transformation of the carbonyl group into a hydrocarbon.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]a)LiAlH4b)Zn-Hg/HClc)NaBH4d)CH3MgICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















