Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > In which soil structure are the particles arr...
Start Learning for Free
In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?
- a)Single grained
- b)Honeycomb
- c)Flocculent
- d)Dispersed
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parall...
Dispersed Structure: In the case of dispersed structure, the particles will have face to face contact. This type of formation is due to net electrical forces between adjacent soil particles at the time of deposition being repulsive in nature. This type of structure is common in fresh water deposits.
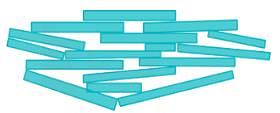
Flocculated Structure: In the case of flocculated structure there will be edge to edge and edge to face contact between the particles. This type of formation is due to the net electrical forces between the adjacent particles at the time of deposition being attractive in nature.
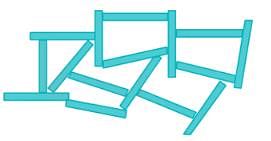
Honeycomb Structure: This type of structure is associated with silt deposits. When silt particles settle out of suspension, in addition to gravitational forces the surface forces also play a significant role.
When particles approach the lower region of suspension they will be attracted by particles deposited as well as the neighbouring particles leading to the formation of arches.
Single grained: This type of structure will be found in the case of coarse grained soil deposits. When such soils settle out of suspension in water, the particles settle independently of each other.
The major force causing their deposition is gravitational and surface forces are too small to produce any effect.
There will be particle-to-particle contact in the deposit.
Most Upvoted Answer
In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parall...
Soil Structure
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles that affects the physical and engineering properties of the soil. There are five types of soil structure, namely single grained, honeycomb, flocculent, dispersed, and blocky.
Dispersed Soil Structure
In dispersed soil structure, the soil particles are arranged more or less parallel to each other. This type of structure is also known as a random structure. The particles are not arranged in any particular pattern, and they do not adhere to each other. Dispersed soil structure is common in clay soils.
Characteristics of Dispersed Soil Structure
The following are the characteristics of dispersed soil structure:
- The soil particles are not arranged in any particular pattern.
- The particles are not bonded to each other.
- The soil has poor permeability and drainage.
- The soil is prone to erosion.
- The soil has poor load-bearing capacity.
Dispersed soil structure is undesirable for engineering purposes because of its poor physical properties. It can lead to settlement, instability, and failure of structures built on it. Therefore, it is essential to identify the soil structure before designing any construction project to avoid any potential problems.
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles that affects the physical and engineering properties of the soil. There are five types of soil structure, namely single grained, honeycomb, flocculent, dispersed, and blocky.
Dispersed Soil Structure
In dispersed soil structure, the soil particles are arranged more or less parallel to each other. This type of structure is also known as a random structure. The particles are not arranged in any particular pattern, and they do not adhere to each other. Dispersed soil structure is common in clay soils.
Characteristics of Dispersed Soil Structure
The following are the characteristics of dispersed soil structure:
- The soil particles are not arranged in any particular pattern.
- The particles are not bonded to each other.
- The soil has poor permeability and drainage.
- The soil is prone to erosion.
- The soil has poor load-bearing capacity.
Dispersed soil structure is undesirable for engineering purposes because of its poor physical properties. It can lead to settlement, instability, and failure of structures built on it. Therefore, it is essential to identify the soil structure before designing any construction project to avoid any potential problems.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In which soil structure are the particles arranged more or less parallel to each other?a)Single grainedb)Honeycombc)Flocculentd)DispersedCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























