Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportiona...
Start Learning for Free
Ionic radii are [2004]
- a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear charge
- b)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear charge
- c)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charge
- d)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear charge
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear ch...
Ion ic r adii are in ver sely pr opor tional to effective nuclear charge.
Ionic radii in the nth orbit is given as
Ionic radii in the nth orbit is given as
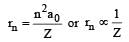
when n = principal quantum number Z-effective nuclear change.
Most Upvoted Answer
Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear ch...
Ionic Radii and Effective Nuclear Charge
Ionic radii refer to the size of ions, which are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The effective nuclear charge is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in an atom or ion. The relationship between ionic radii and effective nuclear charge can be explained as follows:
Inversely Proportional Relationship
Ionic radii are inversely proportional to the effective nuclear charge. This means that as the effective nuclear charge increases, the ionic radii decreases, and vice versa.
Explanation:
- As the effective nuclear charge increases, the attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electrons becomes stronger.
- This increased attraction pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus, resulting in a smaller ionic radius.
- On the other hand, when the effective nuclear charge decreases, the attraction between the nucleus and electrons weakens.
- This weaker attraction allows the electrons to occupy more space and leads to a larger ionic radius.
Reason:
The size of an ion is influenced by the distribution of electrons around the nucleus. When an atom loses an electron to form a cation, the electron-electron repulsion decreases, causing the remaining electrons to be pulled closer to the nucleus. This results in a decrease in the ionic radius. Conversely, when an atom gains an electron to form an anion, the electron-electron repulsion increases, causing the electrons to spread out and resulting in an increase in the ionic radius.
Conclusion:
Ionic radii are inversely proportional to the effective nuclear charge. As the effective nuclear charge increases, the ionic radii decrease, and as the effective nuclear charge decreases, the ionic radii increase. This relationship is due to the changes in electron distribution and the resulting electron-nucleus attraction.
Ionic radii refer to the size of ions, which are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The effective nuclear charge is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in an atom or ion. The relationship between ionic radii and effective nuclear charge can be explained as follows:
Inversely Proportional Relationship
Ionic radii are inversely proportional to the effective nuclear charge. This means that as the effective nuclear charge increases, the ionic radii decreases, and vice versa.
Explanation:
- As the effective nuclear charge increases, the attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electrons becomes stronger.
- This increased attraction pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus, resulting in a smaller ionic radius.
- On the other hand, when the effective nuclear charge decreases, the attraction between the nucleus and electrons weakens.
- This weaker attraction allows the electrons to occupy more space and leads to a larger ionic radius.
Reason:
The size of an ion is influenced by the distribution of electrons around the nucleus. When an atom loses an electron to form a cation, the electron-electron repulsion decreases, causing the remaining electrons to be pulled closer to the nucleus. This results in a decrease in the ionic radius. Conversely, when an atom gains an electron to form an anion, the electron-electron repulsion increases, causing the electrons to spread out and resulting in an increase in the ionic radius.
Conclusion:
Ionic radii are inversely proportional to the effective nuclear charge. As the effective nuclear charge increases, the ionic radii decrease, and as the effective nuclear charge decreases, the ionic radii increase. This relationship is due to the changes in electron distribution and the resulting electron-nucleus attraction.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Question Description
Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Ionic radii are [2004]a)inversely proportional to effective nuclear chargeb)inversely proportional to square of effective nuclear chargec)directly propor tion al to effective n uclear charged)directly proportional to square of effective nuclear chargeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















