Commerce Exam > Commerce Questions > Distinguish between direct personal investiga...
Start Learning for Free
Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation?
Verified Answer
Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral in...
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Commerce courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Commerce courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral in...
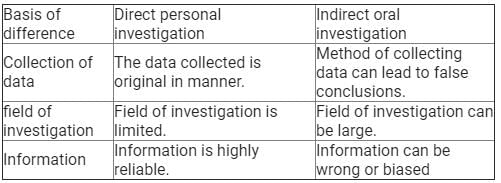
Distinguishing between Direct Personal Investigation and Indirect Oral Investigation
Introduction:
When conducting investigations, there are various methods that can be employed to gather information. Two common approaches are direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation. While both methods aim to gather information, they differ in terms of the means through which the information is obtained. In this response, we will delve into the details of each approach, highlighting their characteristics and differences.
Direct Personal Investigation:
Direct personal investigation refers to the process of gathering information firsthand through personal involvement and observation. This method typically involves an investigator physically visiting the location, interacting with individuals, and examining evidence or documents. Key features of direct personal investigation include:
1. Firsthand information: The investigator collects information directly from the source, allowing for a more accurate and reliable understanding of the situation.
2. Physical presence: This method requires the investigator to be physically present at the location of investigation, enabling them to observe the surroundings and gather evidence.
3. Interpersonal interaction: The investigator engages in face-to-face conversations with relevant individuals, which can provide valuable insights, testimonies, and clarifications.
4. Document examination: Direct personal investigation often involves examining physical documents, such as records, contracts, or financial statements, to gather evidence.
Indirect Oral Investigation:
In contrast to direct personal investigation, indirect oral investigation relies on gathering information through indirect means, such as interviews or discussions with individuals who have knowledge or experience related to the investigation. The key characteristics of indirect oral investigation include:
1. Secondhand information: The investigator collects information from individuals who have knowledge or involvement in the matter but may not be directly related to the incident or location.
2. Verbal communication: Indirect oral investigation typically involves conducting interviews or discussions to obtain information, testimonies, or opinions.
3. Reliance on intermediary sources: The investigator relies on the accounts provided by individuals who may have been witnesses, experts, or have relevant knowledge about the subject matter.
4. Less direct evidence: Compared to direct personal investigation, indirect oral investigation may not provide as much direct physical evidence, as it primarily relies on verbal communication and testimonies.
Conclusion:
In summary, direct personal investigation involves firsthand information gathering through physical presence, observation, interpersonal interaction, and document examination. On the other hand, indirect oral investigation relies on secondhand information obtained through interviews or discussions with relevant individuals. Both methods have their own advantages and limitations, and the choice of approach depends on the specific requirements of the investigation, the availability of resources, and the nature of the information being sought.
Introduction:
When conducting investigations, there are various methods that can be employed to gather information. Two common approaches are direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation. While both methods aim to gather information, they differ in terms of the means through which the information is obtained. In this response, we will delve into the details of each approach, highlighting their characteristics and differences.
Direct Personal Investigation:
Direct personal investigation refers to the process of gathering information firsthand through personal involvement and observation. This method typically involves an investigator physically visiting the location, interacting with individuals, and examining evidence or documents. Key features of direct personal investigation include:
1. Firsthand information: The investigator collects information directly from the source, allowing for a more accurate and reliable understanding of the situation.
2. Physical presence: This method requires the investigator to be physically present at the location of investigation, enabling them to observe the surroundings and gather evidence.
3. Interpersonal interaction: The investigator engages in face-to-face conversations with relevant individuals, which can provide valuable insights, testimonies, and clarifications.
4. Document examination: Direct personal investigation often involves examining physical documents, such as records, contracts, or financial statements, to gather evidence.
Indirect Oral Investigation:
In contrast to direct personal investigation, indirect oral investigation relies on gathering information through indirect means, such as interviews or discussions with individuals who have knowledge or experience related to the investigation. The key characteristics of indirect oral investigation include:
1. Secondhand information: The investigator collects information from individuals who have knowledge or involvement in the matter but may not be directly related to the incident or location.
2. Verbal communication: Indirect oral investigation typically involves conducting interviews or discussions to obtain information, testimonies, or opinions.
3. Reliance on intermediary sources: The investigator relies on the accounts provided by individuals who may have been witnesses, experts, or have relevant knowledge about the subject matter.
4. Less direct evidence: Compared to direct personal investigation, indirect oral investigation may not provide as much direct physical evidence, as it primarily relies on verbal communication and testimonies.
Conclusion:
In summary, direct personal investigation involves firsthand information gathering through physical presence, observation, interpersonal interaction, and document examination. On the other hand, indirect oral investigation relies on secondhand information obtained through interviews or discussions with relevant individuals. Both methods have their own advantages and limitations, and the choice of approach depends on the specific requirements of the investigation, the availability of resources, and the nature of the information being sought.
Attention Commerce Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Commerce study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Commerce.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Similar Commerce Doubts
Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation?
Question Description
Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation? for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation?.
Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation? for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation?.
Solutions for Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Commerce.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation?, a detailed solution for Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation? has been provided alongside types of Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Distinguish between direct personal investigation and indirect oral investigation? tests, examples and also practice Commerce tests.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























