Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > An acidic solution of 'X' does not gi...
Start Learning for Free
An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]
- a)ZnCl2
- b)FeCl3
- c)AlCl3
- d)SnCl2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing...

Given reactions (white precipitate with H2 S in presence of NH4OH) indicate that 'X' should be ZnCl2 which explains all given reactions.
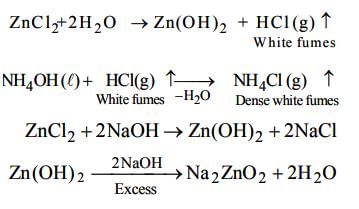
Most Upvoted Answer
An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing...
Identification of Compound X
Acidic Solution of X Does Not Give Precipitate on Passing H2S Through It
This indicates that there is no presence of sulfide ions in the compound X.
X Gives White Precipitate When NH4OH is Added to It
This indicates that the compound X is a metal cation that forms a white precipitate with hydroxide ions.
The White Precipitate Dissolves in Excess of NaOH Solution
This indicates that the white precipitate formed is an amphoteric hydroxide that dissolves in excess of a strong base due to the formation of a soluble complex.
Pure X Fumes in Air
This indicates that the compound X is volatile and can evaporate easily.
Dense White Fumes are Obtained When a Glass Rod Dipped in NH4OH is Put in the Fumes
This indicates that the compound X reacts with NH4OH to form a volatile compound that fumes in air.
Compound X Can Be ZnCl2, FeCl3, AlCl3, or SnCl2
ZnCl2 is the correct answer because it fits all the observations made. Zinc is a metal cation that forms a white precipitate with NH4OH, and the precipitate dissolves in excess NaOH to form a soluble complex. Zinc is also volatile and can fume in air, and it reacts with NH4OH to form a volatile compound that fumes in air. FeCl3 and AlCl3 both give a brown precipitate with H2S, while SnCl2 gives a black precipitate with H2S. Therefore, they do not fit the observation that X does not give a precipitate with H2S.
Acidic Solution of X Does Not Give Precipitate on Passing H2S Through It
This indicates that there is no presence of sulfide ions in the compound X.
X Gives White Precipitate When NH4OH is Added to It
This indicates that the compound X is a metal cation that forms a white precipitate with hydroxide ions.
The White Precipitate Dissolves in Excess of NaOH Solution
This indicates that the white precipitate formed is an amphoteric hydroxide that dissolves in excess of a strong base due to the formation of a soluble complex.
Pure X Fumes in Air
This indicates that the compound X is volatile and can evaporate easily.
Dense White Fumes are Obtained When a Glass Rod Dipped in NH4OH is Put in the Fumes
This indicates that the compound X reacts with NH4OH to form a volatile compound that fumes in air.
Compound X Can Be ZnCl2, FeCl3, AlCl3, or SnCl2
ZnCl2 is the correct answer because it fits all the observations made. Zinc is a metal cation that forms a white precipitate with NH4OH, and the precipitate dissolves in excess NaOH to form a soluble complex. Zinc is also volatile and can fume in air, and it reacts with NH4OH to form a volatile compound that fumes in air. FeCl3 and AlCl3 both give a brown precipitate with H2S, while SnCl2 gives a black precipitate with H2S. Therefore, they do not fit the observation that X does not give a precipitate with H2S.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An acidic solution of 'X' does not give precipitate on passing H2S through it. 'X' gives white precipitate when NH4OH is added to it. The white precipitate dissolves in excess of NaOH solution.Pure 'X' fumes in air and dense white fumes are obtained when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is put in the fumes. Compound 'X' can be [1999]a)ZnCl2b)FeCl3c)AlCl3d)SnCl2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















