Railways Exam > Railways Questions > An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz...
Start Learning for Free
An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:
- a)Inductive
- b)Capacitive
- c)Only resistive
- d)Dependent on RLC elements values
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz ...
In series resonance,
- At the frequencies below resonant frequency, impedance is capacitive
- At resonant frequency, impedance is resistive
- At the frequencies above resonant frequency, impedance is inductive
The impedance - frequency curve is shown below
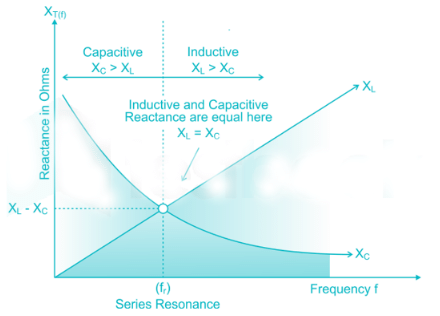
In the given question, resonant frequency (fr) = 150 Hz
Operating frequency (f) = 50 Hz
As operating frequency is less than the resonant frequency, impedance is capacitive.

In the given question, resonant frequency (fr) = 150 Hz
Operating frequency (f) = 50 Hz
As operating frequency is less than the resonant frequency, impedance is capacitive.
Most Upvoted Answer
An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz ...
Impedance in an RLC Series Circuit
In an RLC series circuit, the impedance is the total opposition to the flow of current. It is a combination of resistance, inductance, and capacitance. The impedance in such a circuit can vary depending on the frequency of the applied voltage.
Resonance in an RLC Series Circuit
Resonance occurs in an RLC series circuit when the inductive reactance (XL) and capacitive reactance (XC) cancel each other out, resulting in the minimum impedance. At resonance, the circuit is most efficient in transferring energy from the source to the load. The resonant frequency can be calculated using the formula:
fr = 1 / (2π√(LC))
where fr is the resonant frequency, L is the inductance, and C is the capacitance.
Impedance at 50 Hz
To determine the impedance at a frequency of 50 Hz in a resonating RLC series circuit, we need to compare it to the resonant frequency (150 Hz).
At resonance, the inductive reactance (XL) and capacitive reactance (XC) are equal and cancel each other out. This means that at frequencies above and below resonance, the impedance will be different.
Since 50 Hz is below the resonant frequency of 150 Hz, the capacitive reactance (XC) will be greater than the inductive reactance (XL). As a result, the impedance will be primarily capacitive.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - capacitive.
In an RLC series circuit, the impedance is the total opposition to the flow of current. It is a combination of resistance, inductance, and capacitance. The impedance in such a circuit can vary depending on the frequency of the applied voltage.
Resonance in an RLC Series Circuit
Resonance occurs in an RLC series circuit when the inductive reactance (XL) and capacitive reactance (XC) cancel each other out, resulting in the minimum impedance. At resonance, the circuit is most efficient in transferring energy from the source to the load. The resonant frequency can be calculated using the formula:
fr = 1 / (2π√(LC))
where fr is the resonant frequency, L is the inductance, and C is the capacitance.
Impedance at 50 Hz
To determine the impedance at a frequency of 50 Hz in a resonating RLC series circuit, we need to compare it to the resonant frequency (150 Hz).
At resonance, the inductive reactance (XL) and capacitive reactance (XC) are equal and cancel each other out. This means that at frequencies above and below resonance, the impedance will be different.
Since 50 Hz is below the resonant frequency of 150 Hz, the capacitive reactance (XC) will be greater than the inductive reactance (XL). As a result, the impedance will be primarily capacitive.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - capacitive.

|
Explore Courses for Railways exam
|

|
An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Railways 2025 is part of Railways preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Railways exam syllabus. Information about An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Railways 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Railways 2025 is part of Railways preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Railways exam syllabus. Information about An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Railways 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Railways.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Railways Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An RLC series circuit is resonating at 150 Hz, its impedance at 50 Hz will be:a)Inductiveb)Capacitivec)Only resistived)Dependent on RLC elements valuesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Railways tests.

|
Explore Courses for Railways exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























