Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Explain Golgi apparatus?
Start Learning for Free
Explain Golgi apparatus?
Verified Answer
Explain Golgi apparatus?
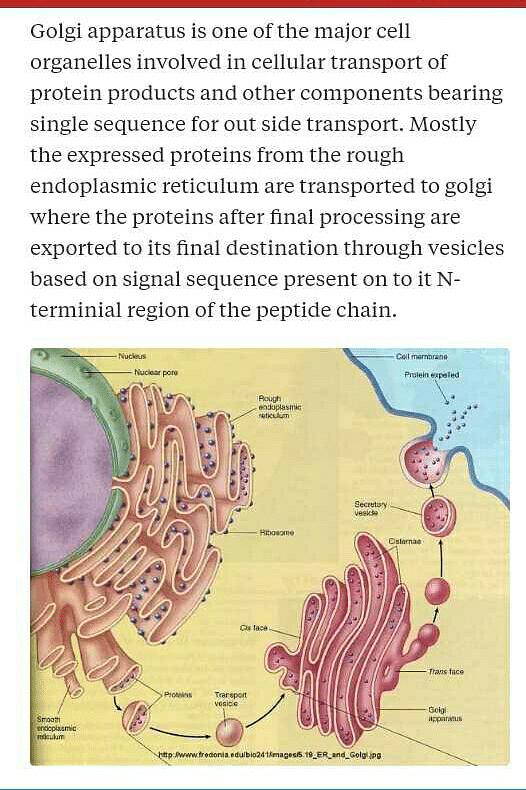
Golgi apparatus, also called Golgi complex or Golgi body, membrane-bound organelle of eukaryotic cells (cells with clearly defined nuclei) that is made up of a series of flattened, stacked pouches called cisternae. The Golgi apparatus is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations. It is located in the cytoplasm next to the endoplasmic reticulum and near the cell nucleus. While many types of cells contain only one or several Golgi apparatus, plant cells can contain hundreds.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Community Answer
Explain Golgi apparatus?
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex or Golgi body, is a vital organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in the processing, packaging, and secretion of proteins and lipids within the cell.
Structure:
- The Golgi apparatus is composed of a series of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae.
- These cisternae are stacked on top of each other, resembling a stack of pancakes.
- The Golgi apparatus also has vesicles that transport molecules to and from the endoplasmic reticulum and other organelles.
Function:
- Protein Processing: The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum. It adds carbohydrate chains to proteins to form glycoproteins.
- Lipid Processing: It also synthesizes lipids and sterols, modifying and packaging them for various cellular functions.
- Vesicle Formation: The Golgi apparatus forms vesicles that transport molecules to different parts of the cell or to the cell membrane for secretion.
- Secretion: It plays a crucial role in the secretion of proteins and lipids from the cell through exocytosis.
Transport within the Golgi:
- Proteins and lipids enter the Golgi apparatus at the cis face and move through the cisternae.
- As they progress through the Golgi, they undergo various modifications and are sorted into specific vesicles at the trans face for transport to their final destinations.
Importance:
- The Golgi apparatus is essential for maintaining cell homeostasis and proper cellular function.
- It is involved in the synthesis of molecules vital for cell structure, signaling, and communication.
In conclusion, the Golgi apparatus is a crucial organelle in eukaryotic cells that plays a vital role in protein and lipid processing, sorting, and secretion. Its intricate structure and functions contribute to the overall functionality and organization of the cell.
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex or Golgi body, is a vital organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in the processing, packaging, and secretion of proteins and lipids within the cell.
Structure:
- The Golgi apparatus is composed of a series of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae.
- These cisternae are stacked on top of each other, resembling a stack of pancakes.
- The Golgi apparatus also has vesicles that transport molecules to and from the endoplasmic reticulum and other organelles.
Function:
- Protein Processing: The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum. It adds carbohydrate chains to proteins to form glycoproteins.
- Lipid Processing: It also synthesizes lipids and sterols, modifying and packaging them for various cellular functions.
- Vesicle Formation: The Golgi apparatus forms vesicles that transport molecules to different parts of the cell or to the cell membrane for secretion.
- Secretion: It plays a crucial role in the secretion of proteins and lipids from the cell through exocytosis.
Transport within the Golgi:
- Proteins and lipids enter the Golgi apparatus at the cis face and move through the cisternae.
- As they progress through the Golgi, they undergo various modifications and are sorted into specific vesicles at the trans face for transport to their final destinations.
Importance:
- The Golgi apparatus is essential for maintaining cell homeostasis and proper cellular function.
- It is involved in the synthesis of molecules vital for cell structure, signaling, and communication.
In conclusion, the Golgi apparatus is a crucial organelle in eukaryotic cells that plays a vital role in protein and lipid processing, sorting, and secretion. Its intricate structure and functions contribute to the overall functionality and organization of the cell.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Explain Golgi apparatus?
Question Description
Explain Golgi apparatus? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Explain Golgi apparatus? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain Golgi apparatus?.
Explain Golgi apparatus? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Explain Golgi apparatus? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain Golgi apparatus?.
Solutions for Explain Golgi apparatus? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Explain Golgi apparatus? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Explain Golgi apparatus?, a detailed solution for Explain Golgi apparatus? has been provided alongside types of Explain Golgi apparatus? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Explain Golgi apparatus? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.