Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > In a zero-order reaction for every 10° ri...
Start Learning for Free
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]
- a)256 times
- b)512 times
- c)64 times
- d)128 times
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the ra...
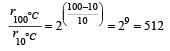
Most Upvoted Answer
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the ra...
In a zero-order reaction, the rate of the reaction does not depend on the concentration of the reactants. The reaction proceeds at a constant rate over time.
For every 10 units of time that pass, the concentration of the reactant will decrease by the same amount. This is because the rate of the reaction is constant and independent of the reactant concentration.
For example, if the initial concentration of the reactant is 100 units, after 10 units of time, the concentration will decrease to 90 units. After another 10 units of time, the concentration will decrease to 80 units, and so on.
This behavior is characteristic of zero-order reactions, where the rate is determined solely by the reaction mechanism and is not influenced by the concentration of the reactants.
For every 10 units of time that pass, the concentration of the reactant will decrease by the same amount. This is because the rate of the reaction is constant and independent of the reactant concentration.
For example, if the initial concentration of the reactant is 100 units, after 10 units of time, the concentration will decrease to 90 units. After another 10 units of time, the concentration will decrease to 80 units, and so on.
This behavior is characteristic of zero-order reactions, where the rate is determined solely by the reaction mechanism and is not influenced by the concentration of the reactants.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]a)256 timesb)512 timesc)64 timesd)128 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















