Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maxi...
Start Learning for Free
In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given by
- a)Difference of the normal stresses
- b)Sum of the normal stresses
- c)Half the sum of the normal stresses
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress...
In case of biaxial stress,
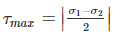
i.e. It is the magnitude of difference between their principal stresses divided by 2.
Most Upvoted Answer
In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress...
In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is not given by any of the options mentioned (a, b, c). The correct answer is option 'D' - None of these.
Explanation:
Biaxial stress refers to a situation where a material is subjected to two different normal stresses in perpendicular directions. In this case, the maximum value of shear stress does not depend on the difference or sum of the normal stresses.
The maximum value of shear stress in biaxial stress can be determined using the following equation:
τ_max = σ_max - σ_min / 2
where,
τ_max is the maximum shear stress
σ_max is the maximum normal stress
σ_min is the minimum normal stress
This equation shows that the maximum shear stress is equal to half the difference between the maximum and minimum normal stresses.
When the material is subjected to pure tensile stress in one direction, the normal stress in that direction is the maximum stress (σ_max), and the normal stress in the perpendicular direction is zero (σ_min = 0). In this case, the maximum shear stress is equal to half the maximum normal stress, which is the tensile stress.
However, in biaxial stress, both normal stresses are non-zero. The maximum normal stress may not be the tensile stress in one direction. Therefore, the maximum shear stress cannot be determined by the difference, sum, or half the sum of the normal stresses.
To determine the maximum shear stress in biaxial stress, the individual normal stresses need to be known. The maximum shear stress occurs on a plane inclined at 45 degrees to the principal planes of stress. The formula to determine the maximum shear stress on this plane is given by:
τ_max = (σ_1 - σ_2) / 2
where,
τ_max is the maximum shear stress
σ_1 is the principal stress with the largest magnitude
σ_2 is the principal stress with the smallest magnitude
Therefore, in the case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is not given by any of the options mentioned (a, b, c). The correct answer is option 'D' - None of these.
Explanation:
Biaxial stress refers to a situation where a material is subjected to two different normal stresses in perpendicular directions. In this case, the maximum value of shear stress does not depend on the difference or sum of the normal stresses.
The maximum value of shear stress in biaxial stress can be determined using the following equation:
τ_max = σ_max - σ_min / 2
where,
τ_max is the maximum shear stress
σ_max is the maximum normal stress
σ_min is the minimum normal stress
This equation shows that the maximum shear stress is equal to half the difference between the maximum and minimum normal stresses.
When the material is subjected to pure tensile stress in one direction, the normal stress in that direction is the maximum stress (σ_max), and the normal stress in the perpendicular direction is zero (σ_min = 0). In this case, the maximum shear stress is equal to half the maximum normal stress, which is the tensile stress.
However, in biaxial stress, both normal stresses are non-zero. The maximum normal stress may not be the tensile stress in one direction. Therefore, the maximum shear stress cannot be determined by the difference, sum, or half the sum of the normal stresses.
To determine the maximum shear stress in biaxial stress, the individual normal stresses need to be known. The maximum shear stress occurs on a plane inclined at 45 degrees to the principal planes of stress. The formula to determine the maximum shear stress on this plane is given by:
τ_max = (σ_1 - σ_2) / 2
where,
τ_max is the maximum shear stress
σ_1 is the principal stress with the largest magnitude
σ_2 is the principal stress with the smallest magnitude
Therefore, in the case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is not given by any of the options mentioned (a, b, c). The correct answer is option 'D' - None of these.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In case of biaxial stress (tensile), the maximum value of shear stress is given bya)Difference of the normal stressesb)Sum of the normal stressesc)Half the sum of the normal stressesd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























