Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 ...
Start Learning for Free
Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.
- a)5.41%
- b)3.54%
- c)4.53%
- d)53.4%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of...
πV = nST for glucose and blood : If isotonic πglucose = πblood;
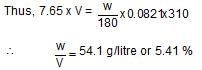
Most Upvoted Answer
Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of...
Calculation of Molar Concentration of Blood
The osmotic pressure of blood is given as 7.65 atm at 310K. To calculate the molar concentration of blood, we can use the relation:
π = MRT
where π is the osmotic pressure, M is the molar concentration, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
On substituting the given values, we get:
7.65 atm = M x 0.0821 L atm mol^-1 K^-1 x 310 K
M = 0.295 M
This means that the molar concentration of blood is 0.295 M.
Calculation of Molar Concentration of Glucose Solution
To find the molar concentration of an aqueous solution of glucose that is isotonic with blood, we need to first understand what isotonicity means. Isotonicity refers to the property of a solution where the concentration of solutes is the same as that of another solution. In this case, we want to find a glucose solution that has the same osmotic pressure as blood, i.e., is isotonic with blood.
The osmotic pressure of a solution is directly proportional to the molar concentration of its solutes. Therefore, if we can find the molar concentration of a glucose solution that has the same osmotic pressure as blood, then that solution will be isotonic with blood.
We know that the molar concentration of blood is 0.295 M. So, we can find the molar concentration of a glucose solution that is isotonic with blood by equating the osmotic pressure of the two solutions. Let the molar concentration of glucose solution be x M.
Using the same relation as before, we get:
7.65 atm = x M x 0.0821 L atm mol^-1 K^-1 x 310 K
x M = 0.795 M
This means that the molar concentration of an aqueous solution of glucose that is isotonic with blood is 0.795 M.
Calculation of Weight-Volume Percentage of Glucose Solution
To find the weight-volume percentage of glucose solution that is isotonic with blood, we need to know the molecular weight of glucose and the density of the solution. The molecular weight of glucose is 180 g/mol, and the density of the solution is assumed to be 1 g/mL.
We can use the relation:
% w/v = (mass of solute/volume of solution) x 100
The mass of solute required to prepare 100 mL of a 0.795 M glucose solution can be calculated as:
mass of glucose = molar concentration x molecular weight x volume
mass of glucose = 0.795 M x 180 g/mol x 0.1 L
mass of glucose = 14.31 g
Therefore, to prepare 100 mL of an aqueous glucose solution that is isotonic with blood, we need to dissolve 14.31 g of glucose in water and make up the volume to 100 mL.
Using the above relation, we get:
% w/v = (14.31 g/100 mL) x 100
% w/v = 5.41%
Therefore, the correct answer is option A, i.e., 5.41%.
The osmotic pressure of blood is given as 7.65 atm at 310K. To calculate the molar concentration of blood, we can use the relation:
π = MRT
where π is the osmotic pressure, M is the molar concentration, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
On substituting the given values, we get:
7.65 atm = M x 0.0821 L atm mol^-1 K^-1 x 310 K
M = 0.295 M
This means that the molar concentration of blood is 0.295 M.
Calculation of Molar Concentration of Glucose Solution
To find the molar concentration of an aqueous solution of glucose that is isotonic with blood, we need to first understand what isotonicity means. Isotonicity refers to the property of a solution where the concentration of solutes is the same as that of another solution. In this case, we want to find a glucose solution that has the same osmotic pressure as blood, i.e., is isotonic with blood.
The osmotic pressure of a solution is directly proportional to the molar concentration of its solutes. Therefore, if we can find the molar concentration of a glucose solution that has the same osmotic pressure as blood, then that solution will be isotonic with blood.
We know that the molar concentration of blood is 0.295 M. So, we can find the molar concentration of a glucose solution that is isotonic with blood by equating the osmotic pressure of the two solutions. Let the molar concentration of glucose solution be x M.
Using the same relation as before, we get:
7.65 atm = x M x 0.0821 L atm mol^-1 K^-1 x 310 K
x M = 0.795 M
This means that the molar concentration of an aqueous solution of glucose that is isotonic with blood is 0.795 M.
Calculation of Weight-Volume Percentage of Glucose Solution
To find the weight-volume percentage of glucose solution that is isotonic with blood, we need to know the molecular weight of glucose and the density of the solution. The molecular weight of glucose is 180 g/mol, and the density of the solution is assumed to be 1 g/mL.
We can use the relation:
% w/v = (mass of solute/volume of solution) x 100
The mass of solute required to prepare 100 mL of a 0.795 M glucose solution can be calculated as:
mass of glucose = molar concentration x molecular weight x volume
mass of glucose = 0.795 M x 180 g/mol x 0.1 L
mass of glucose = 14.31 g
Therefore, to prepare 100 mL of an aqueous glucose solution that is isotonic with blood, we need to dissolve 14.31 g of glucose in water and make up the volume to 100 mL.
Using the above relation, we get:
% w/v = (14.31 g/100 mL) x 100
% w/v = 5.41%
Therefore, the correct answer is option A, i.e., 5.41%.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.a)5.41%b)3.54%c)4.53%d)53.4%Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
















