JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Two equal negative charges –q are fixed...
Start Learning for Free
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q will
- a)execute simple harmonic motion about the origin
- b)move to the origin remain at rest
- c)move to infinity
- d)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a)...
Let us consider the positive charge Q at any instant of time t at a distance x from the origin. It is under the influence of two forces 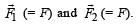 On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force is
On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force is
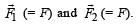 On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force is
On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force isFR = 2F cos θ
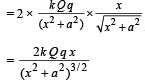
Since FR is not proportional to x, the motion is NOT simple harmonic. The charge Q will accelerate till the origin and gain velocity. At the origin the net force is zero but due to momentum it will cross the origin and more towards left. As it comes on negative x-axis, the force is again towards the origin.
Most Upvoted Answer
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a)...
Repel each other.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Question Description
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q willa)execute simple harmonic motion about the originb)move to the origin remain at restc)move to infinityd)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















