JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficienc...
Start Learning for Free
Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannot
- a)prevent radiation
- b)find ideal sources
- c)reach absolute zero temperature
- d)eliminate friction.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prev...
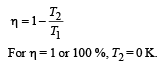
The temperature of 0 K (absolute zero) can not be obtained .
Most Upvoted Answer
Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prev...
Explanation:
The Carnot engine is a theoretical construct that operates on the principles of thermodynamics and is used to determine the maximum efficiency that any heat engine can achieve. It consists of a reversible cycle of four processes: isothermal expansion, adiabatic expansion, isothermal compression, and adiabatic compression. The Carnot engine assumes ideal conditions and has certain limitations that prevent it from achieving 100% efficiency.
1. Radiation:
Radiation is the transfer of heat energy through electromagnetic waves. In an actual engine, some heat is lost through radiation, which reduces its efficiency. However, the Carnot engine assumes that there is no heat loss through radiation, and therefore, this is not the reason why it cannot achieve 100% efficiency.
2. Ideal Sources:
Ideal sources refer to the availability of a heat source and a heat sink at the desired temperatures for the Carnot engine. While the Carnot engine assumes ideal sources, it is not the reason why it cannot achieve 100% efficiency.
3. Absolute Zero Temperature:
Absolute zero temperature is the lowest possible temperature, where all molecular motion ceases. The Carnot engine assumes that the heat source operates at a finite temperature and the heat sink operates at a lower finite temperature, but it does not assume absolute zero temperature. Therefore, the inability to reach absolute zero temperature is not the reason why the Carnot engine cannot achieve 100% efficiency.
4. Friction:
Friction is a force that opposes motion and is present in any mechanical system. In an actual engine, friction causes energy losses, which reduce its efficiency. The Carnot engine assumes that the processes are reversible and therefore do not involve any friction. However, this assumption is not realistic in practical engines, and friction is one of the reasons why the Carnot engine cannot achieve 100% efficiency.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, the correct answer is option 'C' - reach absolute zero temperature. The Carnot engine assumes finite temperatures for the heat source and heat sink, but it does not assume the ability to reach absolute zero temperature. The inability to eliminate friction and other real-world factors such as heat loss through radiation are the primary reasons why the Carnot engine cannot achieve 100% efficiency in practice.
The Carnot engine is a theoretical construct that operates on the principles of thermodynamics and is used to determine the maximum efficiency that any heat engine can achieve. It consists of a reversible cycle of four processes: isothermal expansion, adiabatic expansion, isothermal compression, and adiabatic compression. The Carnot engine assumes ideal conditions and has certain limitations that prevent it from achieving 100% efficiency.
1. Radiation:
Radiation is the transfer of heat energy through electromagnetic waves. In an actual engine, some heat is lost through radiation, which reduces its efficiency. However, the Carnot engine assumes that there is no heat loss through radiation, and therefore, this is not the reason why it cannot achieve 100% efficiency.
2. Ideal Sources:
Ideal sources refer to the availability of a heat source and a heat sink at the desired temperatures for the Carnot engine. While the Carnot engine assumes ideal sources, it is not the reason why it cannot achieve 100% efficiency.
3. Absolute Zero Temperature:
Absolute zero temperature is the lowest possible temperature, where all molecular motion ceases. The Carnot engine assumes that the heat source operates at a finite temperature and the heat sink operates at a lower finite temperature, but it does not assume absolute zero temperature. Therefore, the inability to reach absolute zero temperature is not the reason why the Carnot engine cannot achieve 100% efficiency.
4. Friction:
Friction is a force that opposes motion and is present in any mechanical system. In an actual engine, friction causes energy losses, which reduce its efficiency. The Carnot engine assumes that the processes are reversible and therefore do not involve any friction. However, this assumption is not realistic in practical engines, and friction is one of the reasons why the Carnot engine cannot achieve 100% efficiency.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, the correct answer is option 'C' - reach absolute zero temperature. The Carnot engine assumes finite temperatures for the heat source and heat sink, but it does not assume the ability to reach absolute zero temperature. The inability to eliminate friction and other real-world factors such as heat loss through radiation are the primary reasons why the Carnot engine cannot achieve 100% efficiency in practice.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Question Description
Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency because we cannota)prevent radiationb)find ideal sourcesc)reach absolute zero temperatured)eliminate friction.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























