Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Distinguish between tributary and distributar...
Start Learning for Free
Distinguish between tributary and distributary?
Most Upvoted Answer
Distinguish between tributary and distributary?
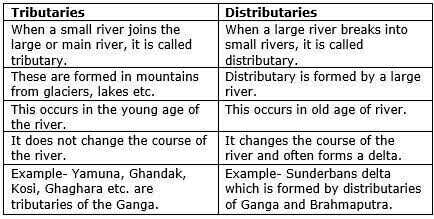
Community Answer
Distinguish between tributary and distributary?
Tributary:
A tributary is a smaller stream or river that flows into a larger stream or river. It contributes its water to the main river, increasing its volume and flow. Tributaries are an essential part of the river network and play a significant role in shaping the landscape and hydrology of a region. Here are some key characteristics and functions of tributaries:
1. Definition:
A tributary is a stream or river that joins a larger river, known as the main stem or trunk, at a confluence. The main stem is typically the main channel that continues to flow downstream and eventually reaches an ocean, sea, or lake.
2. Size and Flow:
Tributaries can vary in size, ranging from small streams to significant rivers. Their flow depends on factors such as the size of the watershed they drain, the amount of precipitation in the area, and the presence of other tributaries.
3. Drainage Basin:
Each tributary has its own drainage basin, which is the area of land where all the water from rainfall and runoff flows into the tributary. These drainage basins combine to form the larger drainage basin of the main river.
4. Contribution to Water Volume:
The primary function of a tributary is to contribute water to the main river. The tributary's flow adds to the volume and velocity of the main river, affecting its hydrology, sediment transport, and overall ecosystem.
5. Erosion and Deposition:
Tributaries erode the land they flow through, transporting sediment, rocks, and minerals downstream. They also deposit sediments, contributing to the formation of floodplains and deltas at the confluence with the main river.
Distributary:
A distributary is a branch or channel that diverts water from a main river or stream into multiple smaller streams or channels. It represents the opposite concept of a tributary, as it splits the flow of water instead of contributing to it. Here are some key characteristics and functions of distributaries:
1. Definition:
A distributary is a channel that branches off from a main river or stream, carrying a portion of its water and dividing the flow into multiple smaller channels or streams.
2. Formation:
Distributaries are formed when a river or stream encounters an obstacle, such as a delta or a levee, that causes it to split into multiple channels. These channels may flow in different directions or spread out across a delta.
3. Water Distribution:
Distributaries distribute the water from the main river or stream to different areas, allowing it to reach a broader region or irrigate multiple fields. They supply water to wetlands, lakes, or other bodies of water along their course.
4. Sediment Deposition:
As distributaries distribute water, they also carry sediment and deposits, which can lead to the formation of river deltas. The sediment-laden water slows down in the distributaries, causing sediments to settle and build up landforms.
5. Navigation and Transportation:
Distributaries can provide alternative routes for navigation and transportation, allowing boats and ships to access different areas or bypass obstacles on the main river. They can also support
A tributary is a smaller stream or river that flows into a larger stream or river. It contributes its water to the main river, increasing its volume and flow. Tributaries are an essential part of the river network and play a significant role in shaping the landscape and hydrology of a region. Here are some key characteristics and functions of tributaries:
1. Definition:
A tributary is a stream or river that joins a larger river, known as the main stem or trunk, at a confluence. The main stem is typically the main channel that continues to flow downstream and eventually reaches an ocean, sea, or lake.
2. Size and Flow:
Tributaries can vary in size, ranging from small streams to significant rivers. Their flow depends on factors such as the size of the watershed they drain, the amount of precipitation in the area, and the presence of other tributaries.
3. Drainage Basin:
Each tributary has its own drainage basin, which is the area of land where all the water from rainfall and runoff flows into the tributary. These drainage basins combine to form the larger drainage basin of the main river.
4. Contribution to Water Volume:
The primary function of a tributary is to contribute water to the main river. The tributary's flow adds to the volume and velocity of the main river, affecting its hydrology, sediment transport, and overall ecosystem.
5. Erosion and Deposition:
Tributaries erode the land they flow through, transporting sediment, rocks, and minerals downstream. They also deposit sediments, contributing to the formation of floodplains and deltas at the confluence with the main river.
Distributary:
A distributary is a branch or channel that diverts water from a main river or stream into multiple smaller streams or channels. It represents the opposite concept of a tributary, as it splits the flow of water instead of contributing to it. Here are some key characteristics and functions of distributaries:
1. Definition:
A distributary is a channel that branches off from a main river or stream, carrying a portion of its water and dividing the flow into multiple smaller channels or streams.
2. Formation:
Distributaries are formed when a river or stream encounters an obstacle, such as a delta or a levee, that causes it to split into multiple channels. These channels may flow in different directions or spread out across a delta.
3. Water Distribution:
Distributaries distribute the water from the main river or stream to different areas, allowing it to reach a broader region or irrigate multiple fields. They supply water to wetlands, lakes, or other bodies of water along their course.
4. Sediment Deposition:
As distributaries distribute water, they also carry sediment and deposits, which can lead to the formation of river deltas. The sediment-laden water slows down in the distributaries, causing sediments to settle and build up landforms.
5. Navigation and Transportation:
Distributaries can provide alternative routes for navigation and transportation, allowing boats and ships to access different areas or bypass obstacles on the main river. They can also support

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Distinguish between tributary and distributary?
Question Description
Distinguish between tributary and distributary? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Distinguish between tributary and distributary? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Distinguish between tributary and distributary?.
Distinguish between tributary and distributary? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Distinguish between tributary and distributary? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Distinguish between tributary and distributary?.
Solutions for Distinguish between tributary and distributary? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Distinguish between tributary and distributary? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Distinguish between tributary and distributary?, a detailed solution for Distinguish between tributary and distributary? has been provided alongside types of Distinguish between tributary and distributary? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Distinguish between tributary and distributary? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























