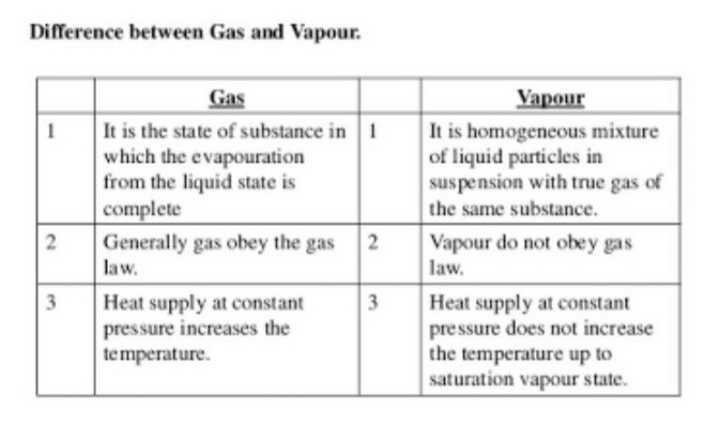
Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Distinguish between gas and vapour
Start Learning for Free
Distinguish between gas and vapour
Verified Answer
Distinguish between gas and vapour
Gas-
1.it is a state of matter.
2.it has experienced phase change.
3.it has low density.
4.it remains as gas only in room temperature.
5. its molecules are separated.
Vapor-
1.it is a state of water between gas and liquid.
2.it has about to experience phase change.
3.it is the result of boiling and evaporation
4.it is measured by the pressure of a gas.
5.at room temperature. vapor can be solid or liquid.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Distinguish between gas and vapour
Difference between Gas and Vapour
Gas and vapour are both forms of matter that exist in the gaseous state. However, there are distinct differences between the two. In this article, we will explore these differences in detail.
Definition
Gas: Gas is a state of matter in which the particles are widely spaced and move freely. It has no definite shape or volume and tends to expand to fill the container it is placed in.
Vapour: Vapour is the gaseous state of a substance that is normally a liquid or solid at room temperature and pressure. It is formed when the substance evaporates or sublimes.
Formation
Gas: Gases are typically formed when a substance reaches its boiling point or when a solid or liquid undergoes a physical or chemical change. For example, when water is heated, it boils and turns into steam, which is a gas.
Vapour: Vapour is formed when a substance evaporates or sublimes. Evaporation occurs when a liquid changes into a gas at a temperature below its boiling point. Sublimation happens when a solid directly transforms into a gas without becoming a liquid first.
State of Matter
Gas: Gas exists in the gaseous state at normal room temperature and pressure. It does not condense into a liquid or solid phase under normal conditions.
Vapour: Vapour is the gaseous state of a substance that is typically a liquid or solid at room temperature and pressure. It can condense back into its liquid or solid form when the temperature or pressure changes.
Examples
Gas: Examples of gases include oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, helium, and carbon dioxide. These substances exist as gases at room temperature and pressure.
Vapour: Examples of vapours include water vapour, steam, and gasoline vapour. These substances are normally liquids at room temperature but can exist in the gaseous state under certain conditions.
Visibility
Gas: Gases are generally invisible to the naked eye. They do not scatter or reflect visible light, which makes them difficult to observe directly.
Vapour: Vapours are often visible as they contain tiny droplets of the substance in the gaseous state. For example, steam is visible when water is boiled.
Conclusion
In summary, the main difference between gas and vapour lies in their formation and the state of matter they represent. Gases are substances that exist in the gaseous state at normal conditions, while vapours are the gaseous form of substances that are typically liquids or solids at room temperature and pressure. Gases are generally invisible, whereas vapours may be visible due to the presence of tiny droplets. Understanding these distinctions can help clarify the nature and behavior of these two forms of matter.
Gas and vapour are both forms of matter that exist in the gaseous state. However, there are distinct differences between the two. In this article, we will explore these differences in detail.
Definition
Gas: Gas is a state of matter in which the particles are widely spaced and move freely. It has no definite shape or volume and tends to expand to fill the container it is placed in.
Vapour: Vapour is the gaseous state of a substance that is normally a liquid or solid at room temperature and pressure. It is formed when the substance evaporates or sublimes.
Formation
Gas: Gases are typically formed when a substance reaches its boiling point or when a solid or liquid undergoes a physical or chemical change. For example, when water is heated, it boils and turns into steam, which is a gas.
Vapour: Vapour is formed when a substance evaporates or sublimes. Evaporation occurs when a liquid changes into a gas at a temperature below its boiling point. Sublimation happens when a solid directly transforms into a gas without becoming a liquid first.
State of Matter
Gas: Gas exists in the gaseous state at normal room temperature and pressure. It does not condense into a liquid or solid phase under normal conditions.
Vapour: Vapour is the gaseous state of a substance that is typically a liquid or solid at room temperature and pressure. It can condense back into its liquid or solid form when the temperature or pressure changes.
Examples
Gas: Examples of gases include oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, helium, and carbon dioxide. These substances exist as gases at room temperature and pressure.
Vapour: Examples of vapours include water vapour, steam, and gasoline vapour. These substances are normally liquids at room temperature but can exist in the gaseous state under certain conditions.
Visibility
Gas: Gases are generally invisible to the naked eye. They do not scatter or reflect visible light, which makes them difficult to observe directly.
Vapour: Vapours are often visible as they contain tiny droplets of the substance in the gaseous state. For example, steam is visible when water is boiled.
Conclusion
In summary, the main difference between gas and vapour lies in their formation and the state of matter they represent. Gases are substances that exist in the gaseous state at normal conditions, while vapours are the gaseous form of substances that are typically liquids or solids at room temperature and pressure. Gases are generally invisible, whereas vapours may be visible due to the presence of tiny droplets. Understanding these distinctions can help clarify the nature and behavior of these two forms of matter.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
Distinguish between gas and vapour
Question Description
Distinguish between gas and vapour for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Distinguish between gas and vapour covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Distinguish between gas and vapour.
Distinguish between gas and vapour for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Distinguish between gas and vapour covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Distinguish between gas and vapour.
Solutions for Distinguish between gas and vapour in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Distinguish between gas and vapour defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Distinguish between gas and vapour, a detailed solution for Distinguish between gas and vapour has been provided alongside types of Distinguish between gas and vapour theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Distinguish between gas and vapour tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.