Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is...
Start Learning for Free
An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]
- a)7.5 cm
- b)10.5 cm
- c)7 cm
- d)10 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed fro...
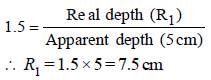
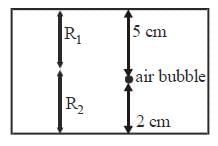
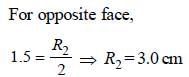
∴ Thickness of the slab = R1 + R2
= 7.5 + 3 = 10.5 cm
= 7.5 + 3 = 10.5 cm
Most Upvoted Answer
An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed fro...
Also known as a lens) will behave differently depending on its position within the slab.
If the air bubble is in the middle of the slab, it will act as a diverging lens. This means that it will cause light rays passing through it to spread out, or diverge. This can be observed by looking through the slab and seeing objects appear smaller and farther away than they actually are.
On the other hand, if the air bubble is closer to one of the surfaces of the slab, it will act as a converging lens. This means that it will cause light rays passing through it to come together, or converge. This can be observed by looking through the slab and seeing objects appear larger and closer than they actually are.
The behavior of the air bubble as a lens is due to the difference in refractive index between the air inside the bubble and the glass slab. The refractive index is a measure of how much light is bent or refracted when it passes through a material. In the case of the air bubble, the difference in refractive index between the air and the glass causes the light rays passing through the bubble to bend, resulting in the lens-like behavior.
It is worth noting that the effect of the air bubble as a lens may be more pronounced if the slab is made of a material with a higher refractive index, such as glass or plastic. Additionally, the size and shape of the air bubble can also affect its lens-like behavior.
If the air bubble is in the middle of the slab, it will act as a diverging lens. This means that it will cause light rays passing through it to spread out, or diverge. This can be observed by looking through the slab and seeing objects appear smaller and farther away than they actually are.
On the other hand, if the air bubble is closer to one of the surfaces of the slab, it will act as a converging lens. This means that it will cause light rays passing through it to come together, or converge. This can be observed by looking through the slab and seeing objects appear larger and closer than they actually are.
The behavior of the air bubble as a lens is due to the difference in refractive index between the air inside the bubble and the glass slab. The refractive index is a measure of how much light is bent or refracted when it passes through a material. In the case of the air bubble, the difference in refractive index between the air and the glass causes the light rays passing through the bubble to bend, resulting in the lens-like behavior.
It is worth noting that the effect of the air bubble as a lens may be more pronounced if the slab is made of a material with a higher refractive index, such as glass or plastic. Additionally, the size and shape of the air bubble can also affect its lens-like behavior.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An air bubble in a glass slab (μ = 1.5) is 5 cmdeep when viewed from one face and 2 cm deepwhen viewed from the opposite face. Thethickness of the slab is [2000]a)7.5 cmb)10.5 cmc)7 cmd)10 cmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























