Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > The total charge induced in a conducting loop...
Start Learning for Free
The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]
- a)the rate of change of magnetic flux
- b)initial magnetic flux only
- c)the total change in magnetic flux
- d)final magnetic flux only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a mag...
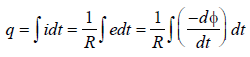
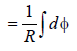 (taking only magnitude of e)
(taking only magnitude of e)Hence, total charge induced in the
conducting loop depends upon the total
change in magnetic flux.
Most Upvoted Answer
The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a mag...
Total Charge Induced in a Conducting Loop
The phenomenon of induced charge in a conducting loop when it is moved in a magnetic field is governed by Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
Understanding the Induction Process
- When a conducting loop moves through a magnetic field, the magnetic flux through the loop changes.
- According to Faraday's law, the induced electromotive force (emf) in a closed loop is directly related to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the loop.
Factors Affecting Induced Charge
- The total charge induced in the loop depends on the total change in magnetic flux (option C).
- It is not just the initial or final magnetic flux that matters, but the total difference between the initial and final states of the magnetic flux.
Key Points to Remember
- Total Change in Magnetic Flux: This is the difference between the magnetic flux at the start and at the end of the movement. The greater this difference, the larger the induced charge.
- Rate of Change vs. Total Change: While the rate of change of magnetic flux is important for calculating induced emf, the total charge induced is ultimately determined by the total change in flux over the entire movement.
Conclusion
In summary, the total charge induced in a conducting loop when moved through a magnetic field is primarily dependent on the total change in magnetic flux, confirming that option C is indeed the correct choice. Understanding this principle is vital in applications like electric generators and transformers, where electromagnetic induction plays a crucial role.
The phenomenon of induced charge in a conducting loop when it is moved in a magnetic field is governed by Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
Understanding the Induction Process
- When a conducting loop moves through a magnetic field, the magnetic flux through the loop changes.
- According to Faraday's law, the induced electromotive force (emf) in a closed loop is directly related to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the loop.
Factors Affecting Induced Charge
- The total charge induced in the loop depends on the total change in magnetic flux (option C).
- It is not just the initial or final magnetic flux that matters, but the total difference between the initial and final states of the magnetic flux.
Key Points to Remember
- Total Change in Magnetic Flux: This is the difference between the magnetic flux at the start and at the end of the movement. The greater this difference, the larger the induced charge.
- Rate of Change vs. Total Change: While the rate of change of magnetic flux is important for calculating induced emf, the total charge induced is ultimately determined by the total change in flux over the entire movement.
Conclusion
In summary, the total charge induced in a conducting loop when moved through a magnetic field is primarily dependent on the total change in magnetic flux, confirming that option C is indeed the correct choice. Understanding this principle is vital in applications like electric generators and transformers, where electromagnetic induction plays a crucial role.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The total charge induced in a conducting loopwhen it is moved in a magnetic field depend on [1992]a)the rate of change of magnetic fluxb)initial magnetic flux onlyc)the total change in magnetic fluxd)final magnetic flux onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























