Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of mod...
Start Learning for Free
A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:
- a)15
- b)19
- c)20
- d)25
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long b...
The slenderness ratio of the wall is lesser of 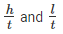
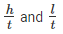
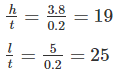
So, slenderness ratio of the wall is 19.
Most Upvoted Answer
A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long b...
To calculate the slenderness ratio of the wall, we need to determine the effective length and the least radius of gyration of the wall.
1. Effective Length:
The effective length of a wall is the distance between the cross walls. In this case, the wall is 5 meters long between cross walls. Therefore, the effective length (Le) is 5 meters.
2. Least Radius of Gyration:
The least radius of gyration (r) is a measure of the ability of the wall to resist buckling. It is given by the formula r = √(I/A), where I is the moment of inertia and A is the cross-sectional area of the wall.
To calculate the moment of inertia, we need to know the dimensions and properties of the cross-section. Given that the wall is made of modular bricks, each brick has a standard size of 190 mm x 90 mm x 90 mm.
3. Cross-Sectional Area:
The cross-sectional area (A) of the wall can be calculated by multiplying the thickness of the wall (200 mm) by the height of the wall (3.8 m). Converting the height to mm, we have:
A = 0.2 m x 3800 mm = 760 mm²
4. Moment of Inertia:
The moment of inertia (I) can be calculated by considering the individual moments of inertia of the bricks and summing them up. For a rectangular cross-section, the moment of inertia is given by the formula I = (b * h^3) / 12, where b is the width and h is the height of the cross-section.
Considering a single brick, the width (b) is 90 mm and the height (h) is 190 mm. Converting the dimensions to meters, we have:
I_brick = (0.09 m * 0.19 m^3) / 12 = 0.000291 m^4
Since the wall is made of multiple bricks, we need to consider the number of bricks in the cross-section. Assuming a joint thickness of 10 mm, the effective width of a single brick is 80 mm.
The number of bricks in the width of the wall (N_b) can be calculated by dividing the width of the wall (5 m) by the effective width of a single brick (0.080 m). Therefore:
N_b = 5 m / 0.080 m = 62.5
Since the number of bricks should be an integer, we can round it up to 63.
The moment of inertia of the wall (I_wall) is given by:
I_wall = N_b * I_brick = 63 * 0.000291 m^4 = 0.018333 m^4
5. Least Radius of Gyration:
The least radius of gyration (r) can now be calculated using the formula r = √(I/A):
r = √(0.018333 m^4 / 0.000760 m^2) = √(24.124) = 4.91 m
6. Slenderness Ratio:
Finally, the slenderness ratio (λ) is given by the formula λ = Le / r:
λ = 5 m / 4.91 m = 1.02
Therefore, the slenderness ratio of the wall is approximately
1. Effective Length:
The effective length of a wall is the distance between the cross walls. In this case, the wall is 5 meters long between cross walls. Therefore, the effective length (Le) is 5 meters.
2. Least Radius of Gyration:
The least radius of gyration (r) is a measure of the ability of the wall to resist buckling. It is given by the formula r = √(I/A), where I is the moment of inertia and A is the cross-sectional area of the wall.
To calculate the moment of inertia, we need to know the dimensions and properties of the cross-section. Given that the wall is made of modular bricks, each brick has a standard size of 190 mm x 90 mm x 90 mm.
3. Cross-Sectional Area:
The cross-sectional area (A) of the wall can be calculated by multiplying the thickness of the wall (200 mm) by the height of the wall (3.8 m). Converting the height to mm, we have:
A = 0.2 m x 3800 mm = 760 mm²
4. Moment of Inertia:
The moment of inertia (I) can be calculated by considering the individual moments of inertia of the bricks and summing them up. For a rectangular cross-section, the moment of inertia is given by the formula I = (b * h^3) / 12, where b is the width and h is the height of the cross-section.
Considering a single brick, the width (b) is 90 mm and the height (h) is 190 mm. Converting the dimensions to meters, we have:
I_brick = (0.09 m * 0.19 m^3) / 12 = 0.000291 m^4
Since the wall is made of multiple bricks, we need to consider the number of bricks in the cross-section. Assuming a joint thickness of 10 mm, the effective width of a single brick is 80 mm.
The number of bricks in the width of the wall (N_b) can be calculated by dividing the width of the wall (5 m) by the effective width of a single brick (0.080 m). Therefore:
N_b = 5 m / 0.080 m = 62.5
Since the number of bricks should be an integer, we can round it up to 63.
The moment of inertia of the wall (I_wall) is given by:
I_wall = N_b * I_brick = 63 * 0.000291 m^4 = 0.018333 m^4
5. Least Radius of Gyration:
The least radius of gyration (r) can now be calculated using the formula r = √(I/A):
r = √(0.018333 m^4 / 0.000760 m^2) = √(24.124) = 4.91 m
6. Slenderness Ratio:
Finally, the slenderness ratio (λ) is given by the formula λ = Le / r:
λ = 5 m / 4.91 m = 1.02
Therefore, the slenderness ratio of the wall is approximately

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A 200 mm thick brick masonry wall made of modular bricks is 5 m long between cross walls and 3.8 m clear height between RCC slabs at top and bottom. The slenderness ratio of the wall is:a)15b)19c)20d)25Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























