JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Imagine a light planet revolving around a ver...
Start Learning for Free
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2
- a)T2 is proportional to R3
- b)T2 is proportional to R7/2
- c)T2 is proportional to R3/2
- d)T2 is proportional to R3/73
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circu...
KEY CONCEPT : The centripetal force is provided by the gravitational force of attraction mRω2 = GMωR–5/2
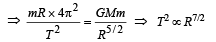
Most Upvoted Answer
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circu...
If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R, it means that the strength of the gravitational force increases as the distance between the planet and the star increases. This is contrary to the inverse square law of gravity, where the force of attraction decreases as the distance increases.
In this scenario, the planet would experience a stronger gravitational force when it is farther from the star and a weaker gravitational force when it is closer to the star. This would result in a peculiar orbit for the planet.
During its orbit, the planet would experience a greater gravitational pull from the star when it is farthest away, causing it to accelerate and move faster. As it moves closer to the star, the gravitational force weakens, causing the planet to decelerate and slow down. This would result in an uneven orbital speed throughout its revolution.
The planet would spend less time in the closer regions of its orbit, where the gravitational force is weaker, and more time in the farther regions, where the gravitational force is stronger. This would lead to an eccentric orbit, where the planet's distance from the star varies significantly during its revolution.
Furthermore, the period of revolution T would be affected by this unusual gravitational force. Since the planet would be moving faster when it is farther from the star, it would cover more distance in less time. Conversely, when the planet is closer to the star, it would cover less distance in more time. As a result, the period of revolution T would not remain constant but would vary throughout the orbit.
Overall, the planet's orbit around the massive star would be irregular, with varying distances and speeds. It would experience a stronger gravitational force when farther from the star and a weaker gravitational force when closer, leading to an eccentric orbit and a non-constant period of revolution.
In this scenario, the planet would experience a stronger gravitational force when it is farther from the star and a weaker gravitational force when it is closer to the star. This would result in a peculiar orbit for the planet.
During its orbit, the planet would experience a greater gravitational pull from the star when it is farthest away, causing it to accelerate and move faster. As it moves closer to the star, the gravitational force weakens, causing the planet to decelerate and slow down. This would result in an uneven orbital speed throughout its revolution.
The planet would spend less time in the closer regions of its orbit, where the gravitational force is weaker, and more time in the farther regions, where the gravitational force is stronger. This would lead to an eccentric orbit, where the planet's distance from the star varies significantly during its revolution.
Furthermore, the period of revolution T would be affected by this unusual gravitational force. Since the planet would be moving faster when it is farther from the star, it would cover more distance in less time. Conversely, when the planet is closer to the star, it would cover less distance in more time. As a result, the period of revolution T would not remain constant but would vary throughout the orbit.
Overall, the planet's orbit around the massive star would be irregular, with varying distances and speeds. It would experience a stronger gravitational force when farther from the star and a weaker gravitational force when closer, leading to an eccentric orbit and a non-constant period of revolution.
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2a)T2 is proportional to R3b)T2 is proportional to R7/2c)T2 is proportional to R3/2d)T2 is proportional to R3/73Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























