JEE Exam > JEE Questions > A wind-powered generator converts wind energy...
Start Learning for Free
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional to
- a)v
- b)v2
- c)v3
- d)v4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. ...
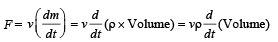

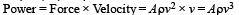
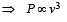
Most Upvoted Answer
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. ...
Wind Energy Conversion
Wind-powered generators are devices that convert wind energy into electrical energy. They typically consist of a rotor with blades, a generator, and various other components. The rotor blades capture the kinetic energy of the wind and transfer it to the generator, where it is converted into electrical energy.
Proportional to Wind Speed
The electrical power output of a wind-powered generator is proportional to the wind speed. This means that as the wind speed increases, the power output of the generator also increases. The relationship between wind speed and power output can be expressed as a mathematical equation. Let's explore the options provided to determine the correct relationship.
a) v
b) v^2
c) v^3
d) v^4
Exploring the Options
a) v: If the power output is proportional to the wind speed (v), it means that doubling the wind speed will double the power output. However, this is not consistent with how wind-powered generators actually work.
b) v^2: If the power output is proportional to the square of the wind speed (v^2), it means that doubling the wind speed will quadruple the power output. This is closer to reality, as wind-powered generators do exhibit a quadratic relationship between wind speed and power output. However, it is not the correct answer.
c) v^3: If the power output is proportional to the cube of the wind speed (v^3), it means that doubling the wind speed will increase the power output by a factor of eight. This is a more accurate representation of the relationship between wind speed and power output for wind-powered generators. Therefore, option 'C' is the correct answer.
d) v^4: If the power output is proportional to the fourth power of the wind speed (v^4), it means that doubling the wind speed will increase the power output by a factor of sixteen. While this relationship may hold true for certain physical phenomena, it does not accurately describe the behavior of wind-powered generators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the electrical power output of a wind-powered generator is proportional to the cube of the wind speed (v^3). This means that as the wind speed increases, the power output of the generator increases exponentially. Option 'C' is the correct answer in this case.
Wind-powered generators are devices that convert wind energy into electrical energy. They typically consist of a rotor with blades, a generator, and various other components. The rotor blades capture the kinetic energy of the wind and transfer it to the generator, where it is converted into electrical energy.
Proportional to Wind Speed
The electrical power output of a wind-powered generator is proportional to the wind speed. This means that as the wind speed increases, the power output of the generator also increases. The relationship between wind speed and power output can be expressed as a mathematical equation. Let's explore the options provided to determine the correct relationship.
a) v
b) v^2
c) v^3
d) v^4
Exploring the Options
a) v: If the power output is proportional to the wind speed (v), it means that doubling the wind speed will double the power output. However, this is not consistent with how wind-powered generators actually work.
b) v^2: If the power output is proportional to the square of the wind speed (v^2), it means that doubling the wind speed will quadruple the power output. This is closer to reality, as wind-powered generators do exhibit a quadratic relationship between wind speed and power output. However, it is not the correct answer.
c) v^3: If the power output is proportional to the cube of the wind speed (v^3), it means that doubling the wind speed will increase the power output by a factor of eight. This is a more accurate representation of the relationship between wind speed and power output for wind-powered generators. Therefore, option 'C' is the correct answer.
d) v^4: If the power output is proportional to the fourth power of the wind speed (v^4), it means that doubling the wind speed will increase the power output by a factor of sixteen. While this relationship may hold true for certain physical phenomena, it does not accurately describe the behavior of wind-powered generators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the electrical power output of a wind-powered generator is proportional to the cube of the wind speed (v^3). This means that as the wind speed increases, the power output of the generator increases exponentially. Option 'C' is the correct answer in this case.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electrical energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional toa)vb)v2c)v3d)v4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















