JEE Exam > JEE Questions > A dense collection of equal number of electro...
Start Learning for Free
A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.
Q. Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x 1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30, ≈ where these quantities are in proper SI units.
- a)800 nm
- b)600 nm
- c)300 nm
- d)200 nm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is c...
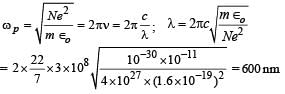
Most Upvoted Answer
A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is c...
Calculation of Plasma Reflection Wavelength
1. Given Data
- Number density of electrons, N = 4 x 10^27 m^-3
- Permittivity of free space, ε0 = 10^-11 C^2/Nm^2
- Mass of electron, m = 10^-30 kg
2. Plasma Frequency Formula
- The plasma frequency, ωp, is given by the formula:
ωp = √(N * e^2 / ε0 * m)
3. Substitute Values
- Charge of electron, e = 1.6 x 10^-19 C
- Using the formula, we get:
ωp = √(4 x 10^27 * (1.6 x 10^-19)^2 / (10^-11) * 10^-30)
4. Calculate Plasma Frequency
- ωp = √(6.4 x 10^8 / 10^-41) = 8 x 10^14 rad/s
5. Wavelength Calculation
- The speed of light, c = 3 x 10^8 m/s
- Wavelength, λ = c / ωp
- Substituting the values, we get:
λ = 3 x 10^8 / 8 x 10^14 = 3.75 x 10^-7 m = 375 nm
Therefore, the plasma reflection will occur at a wavelength of 375 nm, which is closest to option (b) 600 nm.
1. Given Data
- Number density of electrons, N = 4 x 10^27 m^-3
- Permittivity of free space, ε0 = 10^-11 C^2/Nm^2
- Mass of electron, m = 10^-30 kg
2. Plasma Frequency Formula
- The plasma frequency, ωp, is given by the formula:
ωp = √(N * e^2 / ε0 * m)
3. Substitute Values
- Charge of electron, e = 1.6 x 10^-19 C
- Using the formula, we get:
ωp = √(4 x 10^27 * (1.6 x 10^-19)^2 / (10^-11) * 10^-30)
4. Calculate Plasma Frequency
- ωp = √(6.4 x 10^8 / 10^-41) = 8 x 10^14 rad/s
5. Wavelength Calculation
- The speed of light, c = 3 x 10^8 m/s
- Wavelength, λ = c / ωp
- Substituting the values, we get:
λ = 3 x 10^8 / 8 x 10^14 = 3.75 x 10^-7 m = 375 nm
Therefore, the plasma reflection will occur at a wavelength of 375 nm, which is closest to option (b) 600 nm.
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A dense collection of equal number of electrons and positive ions is called neutral plasma. Certain solids containing fixed positive ions surrounded by free electrons can be treated as neutral plasma. Let ‘N’ be the number density of free electrons, each of mass ‘m’. When the electrons are subjected to an electric field, they are displaced relatively away from the heavy positive ions. If the electric field becomes zero, the electrons begin to oscillate about the positive ions with a natural angular frequency ‘ωp’ which is called the plasma frequency. To sustain the oscillations, a time varying electric field needs to be applied that has an angular frequency ω, where a part of the energy is absorbed and a part of it is reflected. As ω approaches ωp all the free electrons are set to resonance together and all the energy is reflected. This is the explanation of high reflectivity of metals.Q.Estimate the wavelength at which plasma reflection will occur for a metal having the density of electrons N ≈ 4 x1027 m–3. Taking ε0 = 10–11 and mass m ≈ 10–30,≈where these quantities are in proper SI units.a)800 nmb)600 nmc)300 nmd)200 nmCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























