Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) T...
Start Learning for Free
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
Aidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as follows
The proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.
However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds as
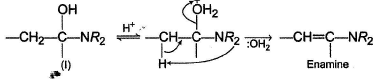
Enamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.
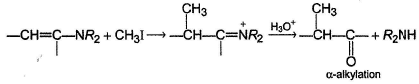
However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds as
Enamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.
Q.
What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?
- a)Reaction occur at very fast rate
- b)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilic
- c)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easily
- d)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a pa...
At very low pH (highly acidic condition), amines get protonated and its nucleophilic character is lost.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAidehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines in slightly acidic condition. A typical reaction mechanism with a primary amine is as followsThe proper pH control is crucial to imine formation otherwise reaction does not proceed at appreciable rate.However, if a secondary amine is reacted, no hydrogen is left on nitrogen on intermediate (I) for the deprotonation in step II. Hence, the reaction proceeds asEnamine is a suitable intermediate route for α-alkyiation of a carbonyl compound.Q.What happens if imine form ation is carried out at very low pH?a)Reaction occur at very fast rateb)Amine gets protonated and becomes non-nucleophilicc)Imine formed gets hydrolysed very easilyd)Imine formed gets protonated favouring backward reactionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















