Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with...
Start Learning for Free
Passage I
The following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:
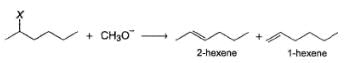
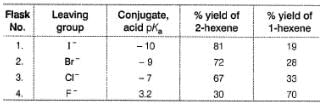
From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.
Q.
Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude that
- a)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexene
- b)Leaving group is not important in E2 reaction
- c)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.
- d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yield
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substi...
Fluorine being the poorest leaving group, major product is one that is formed at fastest rate,

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O-to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q.Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude thata)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexeneb)Leaving group is not important in E2 reactionc)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yieldCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















