Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross section...
Start Learning for Free
A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of the
required force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction is
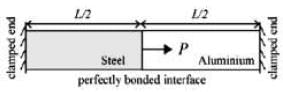
required force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction is

- a)70
- b)140
- c)210
- d)280
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by b...


|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m2 is made by bonding Steel (Young’s modulus = 210 GPa) and Aluminium (Young’s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10−6 in Steel bar and compressive axial strain of magnitude10−6 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of therequired force P (in kN.) along the indicated direction isa)70b)140c)210d)280Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























