Physics Exam > Physics Questions > In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the ...
Start Learning for Free
In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.
Select one:
Select one:
- a)any of the above depending upon the working substance
- b)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigerator
- c)same as that absorbed from the contents
- d)more than that absorbed from the contents
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Selec...
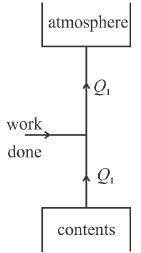
Q1 = W + Q2
Hence Q1 > Q2.
The correct answer is: more than that absorbed from the contents
Most Upvoted Answer
In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Selec...
Heat Exhausted from a Refrigerator
Introduction:
A refrigerator is a common household appliance used to cool and preserve food and other perishable items. It operates on the principle of heat transfer, where heat is removed from the contents of the refrigerator and exhausted to the outer atmosphere. In this question, we are asked to determine the relationship between the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere and the heat absorbed from the contents of the refrigerator.
Explanation:
To understand why the correct answer is option 'D' (more than that absorbed from the contents), let's explore the working principle of a refrigerator.
1. Refrigeration Cycle:
A refrigerator operates based on the refrigeration cycle, which consists of four main components: a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve, and an evaporator. This cycle allows the refrigerator to remove heat from the inside and transfer it to the outside.
2. Heat Transfer:
The refrigeration cycle involves the transfer of heat from the contents of the refrigerator to the outer atmosphere. This heat transfer occurs in two stages:
a. Heat Absorption:
Inside the refrigerator, the evaporator absorbs heat from the contents, cooling them down. This heat transfer process is achieved by circulating a refrigerant, typically a gas or a liquid, through the evaporator coils. The refrigerant evaporates by absorbing heat from the contents, thereby cooling them.
b. Heat Rejection:
After absorbing heat from the contents, the refrigerant vapor is compressed by the compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature. The hot refrigerant then flows into the condenser coils located at the back or bottom of the refrigerator. In the condenser, the refrigerant releases heat to the outer atmosphere, cooling down and condensing back into a liquid state.
3. Conservation of Energy:
According to the principle of conservation of energy, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere must be greater than the heat absorbed from the contents of the refrigerator. This is because the refrigerator requires additional energy, usually in the form of electricity, to drive the refrigeration cycle. This energy is used to power the compressor, which increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, facilitating heat transfer to the outer atmosphere.
4. Conclusion:
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'D' (more than that absorbed from the contents). The refrigerator expels more heat to the outer atmosphere than it absorbs from the contents due to the additional energy input required to drive the refrigeration cycle. This excess heat is a byproduct of the refrigeration process and is dissipated into the surrounding environment.
Introduction:
A refrigerator is a common household appliance used to cool and preserve food and other perishable items. It operates on the principle of heat transfer, where heat is removed from the contents of the refrigerator and exhausted to the outer atmosphere. In this question, we are asked to determine the relationship between the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere and the heat absorbed from the contents of the refrigerator.
Explanation:
To understand why the correct answer is option 'D' (more than that absorbed from the contents), let's explore the working principle of a refrigerator.
1. Refrigeration Cycle:
A refrigerator operates based on the refrigeration cycle, which consists of four main components: a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve, and an evaporator. This cycle allows the refrigerator to remove heat from the inside and transfer it to the outside.
2. Heat Transfer:
The refrigeration cycle involves the transfer of heat from the contents of the refrigerator to the outer atmosphere. This heat transfer occurs in two stages:
a. Heat Absorption:
Inside the refrigerator, the evaporator absorbs heat from the contents, cooling them down. This heat transfer process is achieved by circulating a refrigerant, typically a gas or a liquid, through the evaporator coils. The refrigerant evaporates by absorbing heat from the contents, thereby cooling them.
b. Heat Rejection:
After absorbing heat from the contents, the refrigerant vapor is compressed by the compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature. The hot refrigerant then flows into the condenser coils located at the back or bottom of the refrigerator. In the condenser, the refrigerant releases heat to the outer atmosphere, cooling down and condensing back into a liquid state.
3. Conservation of Energy:
According to the principle of conservation of energy, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere must be greater than the heat absorbed from the contents of the refrigerator. This is because the refrigerator requires additional energy, usually in the form of electricity, to drive the refrigeration cycle. This energy is used to power the compressor, which increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, facilitating heat transfer to the outer atmosphere.
4. Conclusion:
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'D' (more than that absorbed from the contents). The refrigerator expels more heat to the outer atmosphere than it absorbs from the contents due to the additional energy input required to drive the refrigeration cycle. This excess heat is a byproduct of the refrigeration process and is dissipated into the surrounding environment.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In a refrigerator, the heat exhausted to the outer atmosphere is.Select one:a)any of the above depending upon the working substanceb)less than that absorbed from the contents of refrigeratorc)same as that absorbed from the contentsd)more than that absorbed from the contentsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















