JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI f...
Start Learning for Free
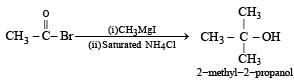
Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl gives
- a)2-methyl-2propanol
- b)acetamide
- c)acetone
- d)acetyl iodide
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with...
Most Upvoted Answer
Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with...
Reaction Overview:
- Acetyl bromide reacts with excess CH3MgI (Grignard reagent) to form a ketone intermediate.
- The ketone intermediate is then treated with a saturated solution of NH4Cl to give 2-methyl-2-propanol.
Reaction Steps:
Step 1: Formation of Grignard reagent
- CH3MgI is prepared by reacting methyl iodide (CH3I) with magnesium (Mg).
- The reaction occurs as follows:
CH3I + Mg → CH3MgI
Step 2: Reaction of Acetyl bromide with CH3MgI
- Acetyl bromide (CH3COBr) reacts with the Grignard reagent (CH3MgI) to form a ketone intermediate.
- The reaction occurs as follows:
CH3COBr + CH3MgI → CH3COCH3
Step 3: Treatment with NH4Cl
- The ketone intermediate (CH3COCH3) is treated with a saturated solution of NH4Cl to give 2-methyl-2-propanol.
- The reaction occurs as follows:
CH3COCH3 + NH4Cl → (CH3)3COH
Explanation:
- Acetyl bromide (CH3COBr) reacts with the Grignard reagent (CH3MgI) to form a ketone intermediate, acetone (CH3COCH3).
- The reaction between acetyl bromide and the Grignard reagent is a nucleophilic addition reaction. The nucleophilic carbon of the Grignard reagent attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of acetyl bromide. This leads to the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate, which subsequently collapses to form the ketone.
- The ketone intermediate, acetone, is then treated with a saturated solution of NH4Cl. This treatment results in the formation of 2-methyl-2-propanol ((CH3)3COH) through a reduction reaction.
- The saturated solution of NH4Cl serves as a source of H+ ions, which act as a reducing agent in the reaction. The H+ ions react with the carbonyl oxygen of the ketone, causing it to be reduced to a hydroxyl group (-OH). This results in the formation of 2-methyl-2-propanol.
- The final product, 2-methyl-2-propanol, is a tertiary alcohol with a branched structure.
Conclusion:
- The reaction of acetyl bromide with excess CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl leads to the formation of 2-methyl-2-propanol.
- This reaction demonstrates the use of Grignard reagents and reduction reactions in organic synthesis.
- Acetyl bromide reacts with excess CH3MgI (Grignard reagent) to form a ketone intermediate.
- The ketone intermediate is then treated with a saturated solution of NH4Cl to give 2-methyl-2-propanol.
Reaction Steps:
Step 1: Formation of Grignard reagent
- CH3MgI is prepared by reacting methyl iodide (CH3I) with magnesium (Mg).
- The reaction occurs as follows:
CH3I + Mg → CH3MgI
Step 2: Reaction of Acetyl bromide with CH3MgI
- Acetyl bromide (CH3COBr) reacts with the Grignard reagent (CH3MgI) to form a ketone intermediate.
- The reaction occurs as follows:
CH3COBr + CH3MgI → CH3COCH3
Step 3: Treatment with NH4Cl
- The ketone intermediate (CH3COCH3) is treated with a saturated solution of NH4Cl to give 2-methyl-2-propanol.
- The reaction occurs as follows:
CH3COCH3 + NH4Cl → (CH3)3COH
Explanation:
- Acetyl bromide (CH3COBr) reacts with the Grignard reagent (CH3MgI) to form a ketone intermediate, acetone (CH3COCH3).
- The reaction between acetyl bromide and the Grignard reagent is a nucleophilic addition reaction. The nucleophilic carbon of the Grignard reagent attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of acetyl bromide. This leads to the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate, which subsequently collapses to form the ketone.
- The ketone intermediate, acetone, is then treated with a saturated solution of NH4Cl. This treatment results in the formation of 2-methyl-2-propanol ((CH3)3COH) through a reduction reaction.
- The saturated solution of NH4Cl serves as a source of H+ ions, which act as a reducing agent in the reaction. The H+ ions react with the carbonyl oxygen of the ketone, causing it to be reduced to a hydroxyl group (-OH). This results in the formation of 2-methyl-2-propanol.
- The final product, 2-methyl-2-propanol, is a tertiary alcohol with a branched structure.
Conclusion:
- The reaction of acetyl bromide with excess CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl leads to the formation of 2-methyl-2-propanol.
- This reaction demonstrates the use of Grignard reagents and reduction reactions in organic synthesis.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Question Description
Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl givesa)2-methyl-2propanolb)acetamidec)acetoned)acetyl iodideCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























