JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Which one of the following is reduced with zi...
Start Learning for Free
Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?
- a)Acetamide
- b)Acetic acid
- c)Ethyl acetate
- d)Butan-2-one
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid ...
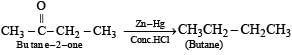
It is Clemmensen’s reduction
Most Upvoted Answer
Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid ...
To determine which compound can be reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon, we need to understand the process of reduction and the properties of the given compounds.
Reduction with Zinc and Hydrochloric Acid:
The reduction of a compound with zinc and hydrochloric acid involves the transfer of hydrogen atoms from the reducing agents (zinc and hydrochloric acid) to the compound, resulting in the formation of a hydrocarbon.
Given Compounds:
a) Acetamide
b) Acetic acid
c) Ethyl acetate
d) Butan-2-one
To identify the compound that can be reduced, we need to consider the presence of functional groups and the reactivity of these functional groups towards reduction.
Acetamide:
Acetamide contains an amide functional group (RCONH2). Amides are not easily reduced by zinc and hydrochloric acid. They require stronger reducing agents or harsher conditions. Therefore, acetamide is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon by zinc and hydrochloric acid.
Acetic Acid:
Acetic acid contains a carboxylic acid functional group (RCOOH). Carboxylic acids can be reduced to aldehydes or alcohols, but they are not directly converted to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, acetic acid is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon in this reaction.
Ethyl Acetate:
Ethyl acetate contains an ester functional group (RCOOR'). Esters can be reduced to alcohols, but they are not directly converted to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, ethyl acetate is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon in this reaction.
Butan-2-one:
Butan-2-one contains a ketone functional group (RCOCH3). Ketones can be reduced to secondary alcohols or further reduced to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, butan-2-one can be reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D) Butan-2-one.
Reduction with Zinc and Hydrochloric Acid:
The reduction of a compound with zinc and hydrochloric acid involves the transfer of hydrogen atoms from the reducing agents (zinc and hydrochloric acid) to the compound, resulting in the formation of a hydrocarbon.
Given Compounds:
a) Acetamide
b) Acetic acid
c) Ethyl acetate
d) Butan-2-one
To identify the compound that can be reduced, we need to consider the presence of functional groups and the reactivity of these functional groups towards reduction.
Acetamide:
Acetamide contains an amide functional group (RCONH2). Amides are not easily reduced by zinc and hydrochloric acid. They require stronger reducing agents or harsher conditions. Therefore, acetamide is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon by zinc and hydrochloric acid.
Acetic Acid:
Acetic acid contains a carboxylic acid functional group (RCOOH). Carboxylic acids can be reduced to aldehydes or alcohols, but they are not directly converted to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, acetic acid is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon in this reaction.
Ethyl Acetate:
Ethyl acetate contains an ester functional group (RCOOR'). Esters can be reduced to alcohols, but they are not directly converted to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, ethyl acetate is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon in this reaction.
Butan-2-one:
Butan-2-one contains a ketone functional group (RCOCH3). Ketones can be reduced to secondary alcohols or further reduced to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, butan-2-one can be reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D) Butan-2-one.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Question Description
Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?a)Acetamideb)Acetic acidc)Ethyl acetated)Butan-2-oneCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























