Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > In an AC transmission line difference in phas...
Start Learning for Free
In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due to
- a)System voltage
- b)Insulators
- c)Resistance of line
- d)Reactance of line
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends ...
In an AC transmission line, difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due to the inductive and capacitive reactance of the transmission lines.
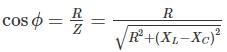
Most Upvoted Answer
In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends ...
Phase Difference in AC Transmission Line
The phase difference in an AC transmission line refers to the difference in phase angle between the voltages at the two ends of the line. This phase difference is primarily caused by the reactive components of the line, namely the reactance.
Reactance of the Line
The reactance of a transmission line is a measure of its opposition to the flow of alternating current due to the presence of inductance and capacitance. The reactance is dependent on the frequency of the AC signal and the physical characteristics of the line.
Inductance and Capacitance
An AC transmission line consists of conductors that are separated by an insulating material, such as air or a dielectric material. Due to the proximity of the conductors and the insulation, the line exhibits both inductance and capacitance.
- Inductance: The conductors of the transmission line act as inductors, which store energy in a magnetic field. The inductance of the line causes the voltage to lag the current.
- Capacitance: The insulation between the conductors acts as a dielectric, which stores energy in an electric field. The capacitance of the line causes the voltage to lead the current.
Effect on Voltage
The inductive reactance and capacitive reactance of the transmission line cause the voltage at the receiving end to be out of phase with the voltage at the sending end. This phase difference is determined by the relative magnitudes of the inductive and capacitive reactances.
- When the inductive reactance dominates, the voltage at the receiving end lags behind the voltage at the sending end.
- When the capacitive reactance dominates, the voltage at the receiving end leads the voltage at the sending end.
System Voltage, Insulators, and Resistance
- System Voltage: The system voltage refers to the magnitude of the voltage supplied by the power generation source. While the system voltage affects the overall magnitude of the voltage in the transmission line, it does not directly cause the phase difference between the two ends of the line.
- Insulators: Insulators are used to support the transmission line conductors and prevent current leakage. While insulators play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the transmission line, they do not directly contribute to the phase difference in voltage.
- Resistance of Line: The resistance of the transmission line causes voltage drops due to the flow of current. However, resistive losses do not cause a phase difference between the voltages at the two ends of the line.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D: Reactance of the line. The phase difference in an AC transmission line is primarily due to the reactive components, specifically the inductive and capacitive reactances, which are inherent in the line's design and characteristics.
The phase difference in an AC transmission line refers to the difference in phase angle between the voltages at the two ends of the line. This phase difference is primarily caused by the reactive components of the line, namely the reactance.
Reactance of the Line
The reactance of a transmission line is a measure of its opposition to the flow of alternating current due to the presence of inductance and capacitance. The reactance is dependent on the frequency of the AC signal and the physical characteristics of the line.
Inductance and Capacitance
An AC transmission line consists of conductors that are separated by an insulating material, such as air or a dielectric material. Due to the proximity of the conductors and the insulation, the line exhibits both inductance and capacitance.
- Inductance: The conductors of the transmission line act as inductors, which store energy in a magnetic field. The inductance of the line causes the voltage to lag the current.
- Capacitance: The insulation between the conductors acts as a dielectric, which stores energy in an electric field. The capacitance of the line causes the voltage to lead the current.
Effect on Voltage
The inductive reactance and capacitive reactance of the transmission line cause the voltage at the receiving end to be out of phase with the voltage at the sending end. This phase difference is determined by the relative magnitudes of the inductive and capacitive reactances.
- When the inductive reactance dominates, the voltage at the receiving end lags behind the voltage at the sending end.
- When the capacitive reactance dominates, the voltage at the receiving end leads the voltage at the sending end.
System Voltage, Insulators, and Resistance
- System Voltage: The system voltage refers to the magnitude of the voltage supplied by the power generation source. While the system voltage affects the overall magnitude of the voltage in the transmission line, it does not directly cause the phase difference between the two ends of the line.
- Insulators: Insulators are used to support the transmission line conductors and prevent current leakage. While insulators play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the transmission line, they do not directly contribute to the phase difference in voltage.
- Resistance of Line: The resistance of the transmission line causes voltage drops due to the flow of current. However, resistive losses do not cause a phase difference between the voltages at the two ends of the line.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D: Reactance of the line. The phase difference in an AC transmission line is primarily due to the reactive components, specifically the inductive and capacitive reactances, which are inherent in the line's design and characteristics.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In an AC transmission line difference in phase of voltage at two ends of the line is due toa)System voltageb)Insulatorsc)Resistance of lined)Reactance of lineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















