Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > When a transition metal ion (usually) is invo...
Start Learning for Free
When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 – y2 and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2g orbitals and those with higher energy are called eg orbitals.
In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes of 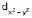 and
and 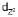 lie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are
lie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are
(i) Pairing may start with 4th electron in t2g orbitals.
(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6th electrons when t2g and eg orbitals are singly filled.
(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6th electrons when t2g and eg orbitals are singly filled.
Q.
Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.
(I) 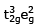 (II)
(II) 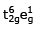 (III)
(III) 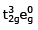 (IV)
(IV) 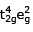
Select the correct code :
- a)I, IV
- b)II, III
- c)III only
- d)III, IV
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral comple...
t32ge2g outer orbital
t32ge0g inner orbital
t42ge2g outer orbital
t2g6e1g inner orbital by excitation of electron.
t32ge0g inner orbital
t42ge2g outer orbital
t2g6e1g inner orbital by excitation of electron.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice When a transition metal ion (usually) is involved in octahedral complex formation, the five degenerate d-orbitals split into two set of degenerate orbitals (3 + 2). Three degenerate orbitals of lower energy (dxy, dyz, dzx) and a set of degenerate orbitals of higher energy (dx2 –y2and dz2). The orbitals with lower energy are called t2gorbitals and those with higher energy are called egorbitals.In octahedral complexes, positive metal ion may be considered to be present at the centre and negative ligands at the corner of a regular octahedron. As lobes ofandlie along the axes, i.e., along the ligands the repulsions are more and so high is the energy. The lobes of the remaining three d-orbitals lie between the axes. i.e., between the ligands. The repulsion between them are less, so lesser the energy. In the octahedral complexes, if metal ion has electrons more than 3 then for pairing them the option are(i) Pairing may start with 4thelectron in t2gorbitals.(ii) Pairing may start normally with 6thelectrons when t2gand egorbitals are singly filled.Q. Which of the following electronic arrangement is /are possible for inner orbital oct complex.(I)(II)(III)(IV)Select the correct code :a)I, IVb)II, IIIc)III onlyd)III, IVCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















