Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The ratio of output change for a given measur...
Start Learning for Free
The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to as
- a)Sensitivity
- b)Linearity
- c)Stability
- d)Fidelity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to...
Sensitivity: It is the change in output to the unit change in input

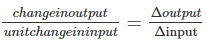
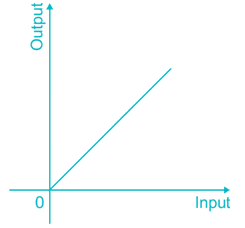
Linearity:The property of an instrument, if output varies linearly according to input is known as linearity. It is the ability to produce the input characteristics symmetrically and linearly. The graphical relationship between input and output is a straight line. It is also a supporting characteristic of accuracy.
Most Upvoted Answer
The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to...
Sensitivity:
Sensitivity refers to the ratio of the output change of a measuring system to the corresponding change in the input or quantity being measured. In other words, it quantifies how responsive a measuring system is to changes in the input.
Linearity:
Linearity refers to the ability of a measuring system to provide output that is directly proportional to the input over a specified range. In a linear system, a doubling of the input would result in a doubling of the output, and so on. However, linearity does not necessarily imply sensitivity.
Stability:
Stability refers to the ability of a measuring system to maintain its performance characteristics over time. It means that the system should produce consistent and accurate measurements without significant drift or deviation. While stability is important for reliable measurements, it is not directly related to the ratio of output change.
Fidelity:
Fidelity refers to the faithfulness or accuracy with which a measuring system reproduces the input signal or quantity being measured. A high-fidelity system accurately represents the input without introducing distortions or inaccuracies. However, fidelity is not specifically related to the ratio of output change.
Explanation:
Among the given options, sensitivity is the correct answer because it directly relates to the ratio of output change. Sensitivity quantifies how much the output of a measuring system changes in response to a given change in the input. A highly sensitive system will exhibit a large output change for a small input change, indicating a high level of responsiveness.
Linearity, stability, and fidelity are also important characteristics of measuring systems, but they do not specifically address the ratio of output change. Linearity ensures a proportional relationship between the input and output, stability ensures consistent performance over time, and fidelity ensures accurate reproduction of the input signal.
In conclusion, sensitivity is the correct option as it directly represents the ratio of output change for a given measuring system.
Sensitivity refers to the ratio of the output change of a measuring system to the corresponding change in the input or quantity being measured. In other words, it quantifies how responsive a measuring system is to changes in the input.
Linearity:
Linearity refers to the ability of a measuring system to provide output that is directly proportional to the input over a specified range. In a linear system, a doubling of the input would result in a doubling of the output, and so on. However, linearity does not necessarily imply sensitivity.
Stability:
Stability refers to the ability of a measuring system to maintain its performance characteristics over time. It means that the system should produce consistent and accurate measurements without significant drift or deviation. While stability is important for reliable measurements, it is not directly related to the ratio of output change.
Fidelity:
Fidelity refers to the faithfulness or accuracy with which a measuring system reproduces the input signal or quantity being measured. A high-fidelity system accurately represents the input without introducing distortions or inaccuracies. However, fidelity is not specifically related to the ratio of output change.
Explanation:
Among the given options, sensitivity is the correct answer because it directly relates to the ratio of output change. Sensitivity quantifies how much the output of a measuring system changes in response to a given change in the input. A highly sensitive system will exhibit a large output change for a small input change, indicating a high level of responsiveness.
Linearity, stability, and fidelity are also important characteristics of measuring systems, but they do not specifically address the ratio of output change. Linearity ensures a proportional relationship between the input and output, stability ensures consistent performance over time, and fidelity ensures accurate reproduction of the input signal.
In conclusion, sensitivity is the correct option as it directly represents the ratio of output change for a given measuring system.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The ratio of output change for a given measuring system is referred to asa)Sensitivityb)Linearityc)Stabilityd)FidelityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















