Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Questions > The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for e...
Start Learning for Free
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by about
- a)64 times
- b)10 times
- c)24 times
- d)32 times
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of tem...
For every 10o C rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. Thus, temperature coefficient of the reaction = 2 when temperature is increased by 50o rate becomes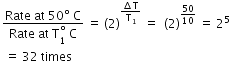
View all questions of this test
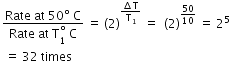
Most Upvoted Answer
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of tem...
°C increase in temperature. This relationship is known as the Arrhenius equation, which states that the rate constant (k) is proportional to the activation energy (Ea) divided by the product of the gas constant (R) and the absolute temperature (T):
k = A * e^(-Ea/RT)
where A is the pre-exponential factor or frequency factor, which is a constant that depends on the specific reaction and represents the number of collisions per unit time that result in a successful reaction.
The exponential term in the equation reflects the temperature dependence of the reaction rate, as higher temperatures increase the probability that reactants will collide with enough energy to overcome the activation barrier and form products.
Therefore, a small increase in temperature can have a significant effect on the reaction rate, especially if the activation energy is relatively low. For example, raising the temperature by 10°C can double the rate of a reaction with an activation energy of 20 kJ/mol, but it may have a smaller effect on a reaction with an activation energy of 80 kJ/mol.
k = A * e^(-Ea/RT)
where A is the pre-exponential factor or frequency factor, which is a constant that depends on the specific reaction and represents the number of collisions per unit time that result in a successful reaction.
The exponential term in the equation reflects the temperature dependence of the reaction rate, as higher temperatures increase the probability that reactants will collide with enough energy to overcome the activation barrier and form products.
Therefore, a small increase in temperature can have a significant effect on the reaction rate, especially if the activation energy is relatively low. For example, raising the temperature by 10°C can double the rate of a reaction with an activation energy of 20 kJ/mol, but it may have a smaller effect on a reaction with an activation energy of 80 kJ/mol.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of tem...
For every 10degree celcius rise of temparature there is there Is 2 times increase in rate of reaction since teparature is incresed 5 times so 2^5 is equals to 32.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Similar Chemistry Doubts
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemistry.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by abouta)64 timesb)10 timesc)24 timesd)32 timesCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemistry tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















